操作系统实验导航
实验一:银行家算法 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46291251/article/details/115384510
实验二:多级队列调度和多级反馈队列调度算法 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46291251/article/details/115530582
实验三:动态分区式内存管理 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46291251/article/details/115772341
实验四:Linux下多进程通信 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46291251/article/details/116274665
实验五:进程通信的三种方式 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46291251/article/details/116301250
实验六:Linux文件系统实验 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46291251/article/details/116423798
实验七:自制简单U盘引导程序 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46291251/article/details/116427629
实验八:磁盘调度算法 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46291251/article/details/116431907
实验九:请求分页系统中的置换算法 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46291251/article/details/116443021
学习笔记:操作系统复习笔记 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46291251/article/details/117086851
背景
- 先进先出(FIFO)页面置换算法
该算法总是淘汰最新进入内存的页面,即选择在内存中驻留时间最久的页面予以淘汰。该算法实现简单,只需把一个进程已调入内存的页面,按先后次序链接成一个队列,并设置一个指针,称为替换指针,使它总是指向最老的页面。
- 最近最久未使用(LRU)页面置换算法
最近最久未使用(LRU)页面置换算法,是根据页面调入内存后的使用情况进行决策的。由于无法预测各页面将来的使用情况,只能利用“最近的过去”作为“最近的将来”的近似, 因此,LRU 置换算法是选择最近最久未使用的页面予以淘汰。该算法赋予每个页面一个访问字段,用来记录一个页面自上次被访问以来所经历的时间 t,当需淘汰一个页面时,选择现有页面中其 t 值最大的,即最近最久未使用的页面予以淘汰。
- 最佳(Optimal)页面置换算法
该算法选择的被淘汰页面,将是以后永远不使用的,或许是在最长(未来)时间内不再被访问的页面。采用该算法,通常可保证获得最低的缺页率。但由于人们目前还无法预知一个进程在内存的若干个页面中,哪一个页面是未来最长时间内不再被访问的,因而该算法是无法实现的,但可以利用该算法去评价其他算法。
题目描述:请求分页系统中的置换算法
1.通过如下方法产生一指令序列,共 320 条指令。
- A. 在[1,32k-2]的指令地址之间随机选取一起点M,访问 M;
- B. 顺序访问M+1;
- C. 在[0,M-1]中随机选取M1,访问 M1;
- D. 顺序访问M1+1;
- E. 在[M1+2,32k-2]中随机选取M2,访问 M2;
- F. 顺序访问M2+1;
- G. 重复 A—F,直到执行 320 次指令。
- H.指令序列变换成页地址流设:(1)页面大小为 1K;(2)用户虚存容量为 32K。
2. 计算并输出下述各种算法在不同内存页块(页块个数范围:8-32)下的命中率。
- A. 先进先出(FIFO)页面置换算法
- B. 最近最久未使用(LRU)页面置换算法
- C. 最佳(Optimal)页面置换算法
提示:
- A.命中率=1-页面失效次数/页地址流长度
- B.本实验中,页地址流长度为 320,页面失效次数为每次访问相应指令时,该指令所对应的页不在内存的次数。
算法设计
整体设计
设置全局变量保存指令的个数和指令数组,在make_instruct()函数中生成随机数填充这个数组。
内存这里用链表来组织,表示如下:
struct node {
int instruct = 0;
int time = 0;
node* next = NULL;
};
instruct表示指令号,time在不同算法中有具体含义。
三种算法对于三个函数,每个函数都是如:double f(int a);的格式,其中参数表示当前内存块大小(8-32),返回值是命中率。
主函数只需对不同的内存块大小调用三个函数并输出结果即可。
产生指令序列
首先写一个函数生成给定范围内的一个随机数,由于需要连续获得多个随机数,这里先在main函数srand一个种子,然后不断调用函数即可。
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
int rand(int min, int max)//产生指定范围[min,max]的随机数。
{
return rand() % (max - min + 1) + min;
}
构造指令序列,只需要简单的按照题目要求一步步做并且循环即可,注意这里只在循环开始处有一次判断,而每次循环会产生6个指令,所以这里将指令数组开大了一点,省去了多次判断。
const int instruct_num = 320; int instruct_arr[instruct_num + 6];
另外,为了输出结果的美观用cout << setw(8)设置输出的宽度以对齐。
void make_instruct() {//产生指令序列
int n = 0;
while (n < instruct_num) {
int M = rand(1,30);
instruct_arr[n++] = M;
instruct_arr[n++] = M + 1;
int M1 = rand(0, M - 1);
instruct_arr[n++] = M1;
instruct_arr[n++] = M1 + 1;
int M2 = rand(M1 + 2, 30);
instruct_arr[n++] = M2;
instruct_arr[n++] = M2 + 1;
}
}
先进先出(FIFO)
这是最基础的,以下的算法都继承这种思想,只是用于淘汰的策略有所变化。
首先新建两个节点Head和TailHead为头节点,其数据域Head->instruct表示当前内存中实际有多少被占用,其next指向第一块被占用的内存。Tail为尾指针,指向内存的尾部。
算法首先是一层循环,遍历所有的(320个)指令。对于每个指令判断是否在内存中,若在则hit置为1。如果在内存中则不做任何操作,不在则要让failure_times加一,然后判断内存是否被占满,若未被占满则直接加入链表,若被占用则要淘汰当前队列中的一个指令,并将当前指令插入内存的合适位置。
这里用到的淘汰算法:先进先出,即找到最先进来的即可,这里我是每次插入到链表尾,故链表头是最先进来的,所以每次都删除链表头后面的第一个指令并将新指令加到链表尾即可,注意每次更新Tail的位置。
最近最久未使用(LRU)
这里只介绍与FIFO不同之处。
- 设立一个变量
clock表示时钟,初始值为999,主循环一次clock就减1.
- 如果当前指令在内存中则将其时间刷新为当前的时钟。
- 淘汰算法:遍历内存队列找到time最大的,将其替换为新的节点即可,新加入的节点time为当前时钟clock
最佳(Optimal)
- 淘汰算法:每次遍历内存队列,对于每个指令,再次遍历全部指令集,找到将来还要多久这条指令会再被执行(下一个出现的位置减去当前位置)。
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
const int instruct_num = 320;
int instruct_arr[instruct_num + 6];
struct node {
int instruct = 0;
int time = 0;
node* next = NULL;
};
int rand(int min, int max)//产生指定范围[min,max]的随机数。
{
return rand() % (max - min + 1) + min;
}
void make_instruct() {//产生指令序列
int n = 0;
while (n < instruct_num) {
int M = rand(1,30);
instruct_arr[n++] = M;
instruct_arr[n++] = M + 1;
int M1 = rand(0, M - 1);
instruct_arr[n++] = M1;
instruct_arr[n++] = M1 + 1;
int M2 = rand(M1 + 2, 30);
instruct_arr[n++] = M2;
instruct_arr[n++] = M2 + 1;
}
}
double C_FIFO(int block_size) {
int failure_times = 0;
node* Head = new node;
node* Tail = Head;
for (int i = 0; i < instruct_num; i++) {
int cur_instruct = instruct_arr[i];
int hit = 0;
for (node* p = Head->next; p != NULL; p = p->next)
if (p->instruct == cur_instruct)
hit = 1;
if (!hit){
failure_times++;
if (Head->instruct >= block_size) //内存已满
Head->next = Head->next->next;
else
Head->instruct++;
Tail->next = new node;
Tail = Tail->next;
Tail->instruct = cur_instruct;
Tail->next = NULL;
}
}
return 1.0 - (double)failure_times / instruct_num;
}
double C_LRU(int block_size) {
int failure_times = 0;
node* Head = new node;
node* Tail = Head;
int clock = 999;
for (int i = 0; i < instruct_num; i++) {
clock--;
int cur_instruct = instruct_arr[i];
int hit = 0;
for (node* p = Head->next; p != NULL; p = p->next)
if (p->instruct == cur_instruct) {
hit = 1;
p->time = clock;//刷新时钟
}
if (!hit) {
failure_times++;
if (Head->instruct >= block_size) { //内存已满
node* t = new node; t->time = -1;
for (node* p = Head->next; p != NULL; p = p->next)//遍历找到最久未使用的
if (p->time > t->time)
t = p;
t->instruct = cur_instruct;
t->time = clock;
}
else {
Head->instruct++;
Tail->next = new node;
Tail = Tail->next;
Tail->instruct = cur_instruct;
Tail->time = clock;
Tail->next = NULL;
}
}
}
return 1.0 - (double)failure_times / instruct_num;
}
double C_Optimal(int block_size) {
int failure_times = 0;
node* Head = new node;
node* Tail = Head;
for (int i = 0; i < instruct_num; i++) {
int cur_instruct = instruct_arr[i];
int hit = 0;
for (node* p = Head->next; p != NULL; p = p->next)
if (p->instruct == cur_instruct)
hit = 1;
if (!hit) {
failure_times++;
if (Head->instruct >= block_size) { //内存已满
//找到每个请求还有多久会被用到
for (node* p = Head->next; p != NULL; p = p->next) {
p->time = 999;
for (int j = i + 1; j < instruct_num; j++)
if (p->instruct == instruct_arr[i]) {
p->time = j - i;
break;
}
}
//找到最久不被用到的淘汰
node* t = new node; t->time = -1;
for (node* p = Head->next; p != NULL; p = p->next)//遍历找到最久未使用的
if (p->time > t->time)
t = p;
t->instruct = cur_instruct;
}
else {
Head->instruct++;
Tail->next = new node;
Tail = Tail->next;
Tail->instruct = cur_instruct;
Tail->next = NULL;
}
}
}
return 1.0 - (double)failure_times / instruct_num;;
}
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
make_instruct();
cout << "指令序列为:" << endl;
int i = 0;
while (i++ < instruct_num) {
cout << instruct_arr[i] << "\t";
if (i % 20 == 0)cout << endl;
}cout << endl << endl;
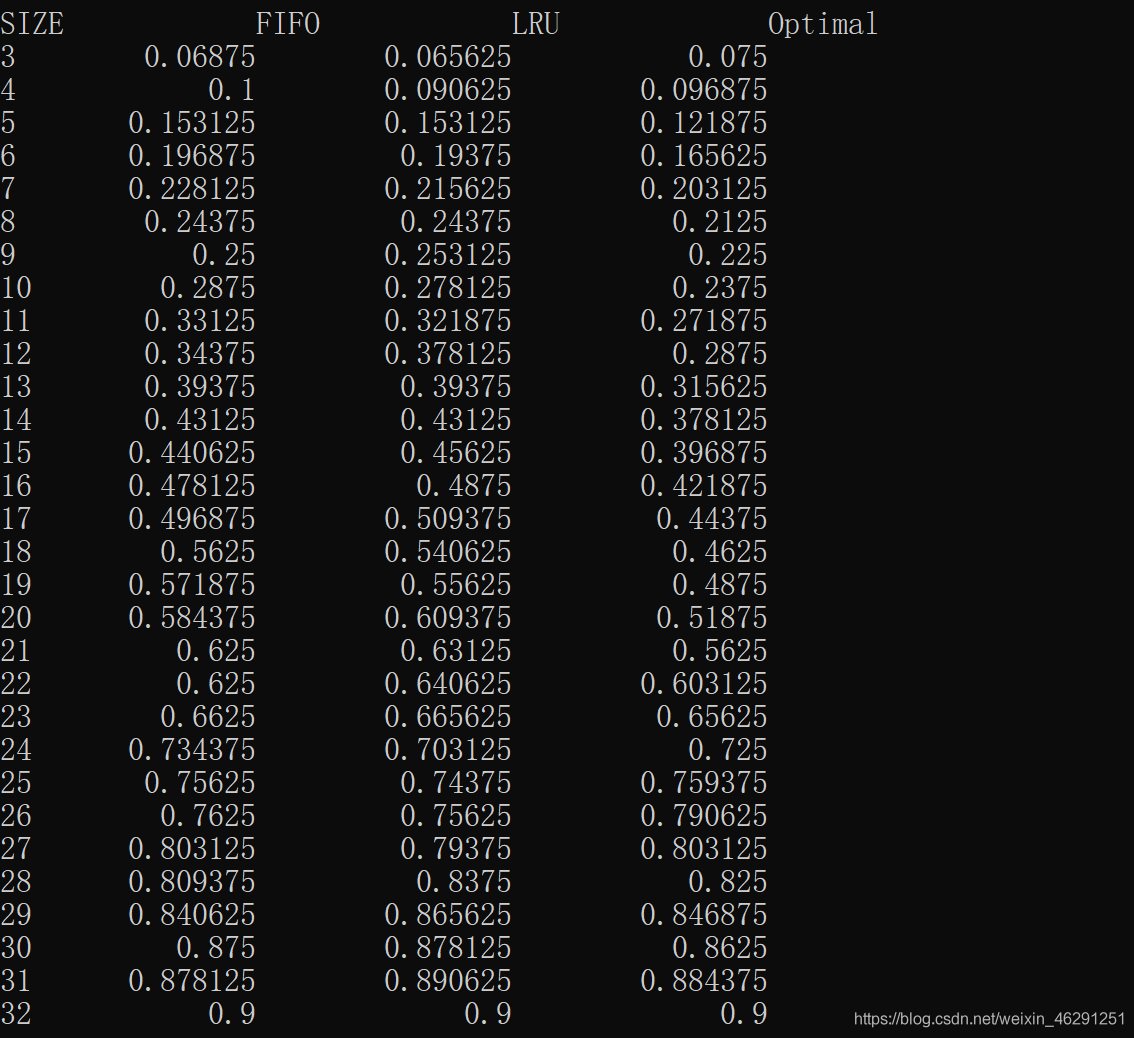
cout << "SIZE\t\t" << "FIFO\t\t" << "LRU\t\t" << "Optimal" << endl;
for (int disk_block_size = 8; disk_block_size <= 32; disk_block_size++) {
cout << disk_block_size << "\t";
cout << setw(8) << C_FIFO(disk_block_size) << "\t";
cout << setw(8) << C_LRU(disk_block_size) << "\t";
cout << setw(8) << C_Optimal(disk_block_size) << "\t";
cout << endl;
}
}
运行结果