详见:
libteam 项目 wiki
libteam ppt
架构
目标:替代 bonding 功能,最终干掉 bonding。
内核中的代码尽可能少。把内核当成是 puppet
控制逻辑在用户空间实现,puppeteer
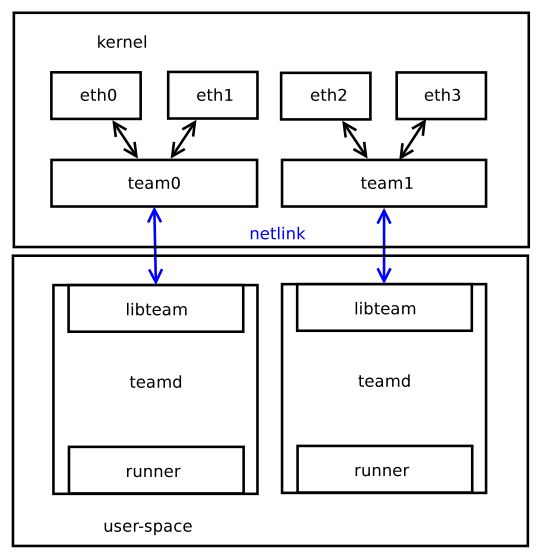
整个项目称为 team project,其中用户空间的代码项目为 libteam,含 libteam 库、teamd daemon、teamd-utils 三个组件。
teamdev driver
从 Linux 内核版本 3.3 开始支持。teamdev driver 遵循以下原则,只做报文的 rx/tx 处理,本身无业务逻辑。
If something can be done in userspace, do it in userspace.
fast-path (1.4KLOC)
netlink 通信(0.6KLOC)user space 配置、改变 teamdev 驱动的行为
user space 从驱动获取端口状态变化等事件
Team 模式一种 mode 一个内核模块
activebackup
broadcast
loadbalance
random
roundrobin
一般称为 teamdev,接口名为 team0 等。
libteam lib
使用 libnl,封装 Team Netlink 通信。用户无需知道任何 Netlink API 相关的信息。
所有消息都来自 driver,并缓存在用户空间,使用者不需要发任何消息就能获取到请求的数据。
同时封装 RT Netlink,用于使用者添加、删除 Teamdev 实例,或添加删除 port,或获取、设置网络接口的硬件 IP 等。
libteam teamd
即 Team daemon,为 libteam 项目的一部分,使用 libteam lib。teamd 跑在后台,一个实例对应一个 Team softdev,用于支持多种多样的逻辑 Team 行为。比如 基础的 round-robin,或更复杂的 active-backup、load-balancing。这些逻辑在 teamd 中称为 runner,每个 Team softdev 只能运行一种 runner。
Team Netlink
有两种类型的消息:Port list 和 option list。
Port list 消息只存在 driver -> lib 方向,只读数据。schema:
port iteminterface index
changed flag,指明该端口任何状态是否有变化。
removed flag,指明端口被删除了
linkup,直接从 ethtool 获取 link 状态
speed,直接从 ethtool 获取 Mbps
duplex,直接从 ethtool 获取 duplex
port item…
port item…
Option list 消息可能存在两个方向。driver -> lib 方向,暴露并传输 driver 数据到 userspace。 lib-> driver 方向,用于通告 driver 哪个 option 的值应变化,应怎么变化。schema 如下:
option itemname,option 名
changed flag
removed flag
type,指明以面 data 域的类型
data,动态类型
port interface index。如果 option 是 per-port 的,那么这个值为对应接口 index。
array index,如果 option 是 array。
option item…
option item…
存在以下消息:
lib 请求 port list
lib 请求 option list
lib 请求 option 值变化
driver port 状态变化事件。net core 通知 dirver 哪些端口状态变化或被删除。
driver option 值变化事件。
第4、5点,使用 netlink multicast facility,用于支撑多用户空间实例。
teamnl,使用 libteam,并封装 Team device Netlink 通信。
Driver
通过 ip 工具集即可添加、删除 team 设备。
1
2# ip link add name team0 type team
# ip link delete team0
创建 team 设备时,如果未指定硬件地址,将生成一个随机的。
同样通过 ip 工具集添加、移除端口。
1
2#ip link set eth0 master team0
#ip link set eth0 nomaster
Team softdev 驱动使用 netdevice 通告机制获取 port 上面的事件,比如 link 状态变化、port 丢失等。当一个 team 设备实例创建时(例如 team0),它就与其他网络设备无异,用户可像普通网络设备那样配置 team0,比如配置 IP 地址、应用 iptables 规则等。不同的地方是它自己不能从收发 skb,它使用其他网络设备(物理端口)。
发送 skb 时,team softdev 通过 port 选择算法选出一个 port,然后使用该 port 的 netdevice 发送 skb。
接收端,team softdev 使用 net core rx 步骤的 rx_handle 钩子拦截报文。bonding、bridging、macvlan 和 openvswitch 使用同样的钩子。通过这个钩子,报文看起来就像是从 teamdev 中接收的。然后 Net 核心代码就将报文视为从 teamdev 中接收的,进行下一步处理。
问题的重点在于如何达到最好的性能,因此 fast path(skb 发送、接收 paths)都是无锁的,只使用 RCU。同时将数据存到内存中,实现最大的局部性和最小的指针解引用。
Options
【TBD】
Modes
每个 mode 实现成一个 module。Team core 代码使用用户空间应用配置的 mode 字符串,调用对应 mode 实现的 handler。这些 handler 定义以下行为:
init,在选择模式后调用,与通常的 init 函数一样,用于分配内存和注册 mode 特有的 option。
exit,反选 mode 后调用。
receive,由接收钩子调用,这个 handler 允许 mode 查看收到的 skb,并可修改 skb。
transmit,由 Team core 发送函数调用。在这里决策发送端口。
port_enter,当一个端口加入 teamdev 时调用
port_leave,当一个端口移除时调用
port_change_mac,当检测到硬件地址发生变化时调用。
目前实现五种模式:
broadcast,Basic mode。将报文发送给所有可能的端口。
roundrobin,Basic mode。一种很简单的端口选择算法,基于端口列表,逐个循环选择端口。这是唯一一种可以不需要用户空间交互就可正常 运行的模式。
random,Basic mode。随机选择端口。
activebackup,在这种模式,只有一个端口处于 active 状态,该端口处理 skb 收发。其他端口都处于 backup 状态。用户空间通过 activeport 选项指定 active 端口。
loadbalance,一个复杂的模式。比如用于 LACP 和用户空间控制收发均衡。使用 hash 识别相同的 skb。Hash 长度 8 比特,所以总共有 256 种类型的 skb。hash 使用 BPF (Berkeley Packet Filter) 机制计算。这个模式使用以下选项:
bpf_hash_func,一个二进制 option,包含 BPF 函数,用于从 skb 计算 hash 值。应用空间可组合和配置 hash 计算函数。例如源、目的 IP 地址、MAC 地址等。
lb_hash_stats 和 lb_port_stats,只读数组选项。暴露 256 种可能的 skb 类型的收发计算器,以及每个端口的收发计算器。用户空间程序可使用这个统计值判断端口的均衡程序,如果均衡程度不够,再进行 hash 算法调整。
lb_stats_refresh_interval,下发统计值到用户空间的频率。
lb_tx_hash_to_port_mapping,用于 hash-to-port 映射的数组选项。允许用户空间应用程序告诉驱动程序某个特定 hash 值的 skb 应选择哪个端口发送。
lb_tx_method,字符串选择,有两个值。hash,告诉驱动使用 hash 值获取发送端口
hash_to_port_mapping,使能 hash_to_port_mapping 功能,并从先前的数组选项获取发送端口。
teamd
libteam 项目的重要部分。如果可能,最好在 teamd 实现功能,而非 Team softdev Linux 驱动。把 teamdev 视为木偶,则 teamd 是操纵 teamdev 的傀儡师。
teamd 的详细命令行参数见 man 8 teamd。
teamd 负责 teamdev 的创建与删除。teamdev 在 teamd 启动的时候创建,在 teamd 退出前删除。teamdev 的名字(比如 team0)通过配置文件指定。
Teamd 主要负责:
配置文件解析
后台 forking 以及诸如 PID 创建、信号处理等相关的事情。在运行 systemd 的系统中不需要,但是 teamd 也需要运行在其他系统。
Team softdev Linux driver 实例的创建与删除。
Libteam 库通信初始化
提供主循环框架,用于 fd 或定时器等的监控与处理。
初始化事件机
端口添加、删除事件处理
初始化链路状态监控器(watcher)
初始化 runner
初始化 D-Bus 接口
添加端口到 teamdev
teamd 被设计成单进程、单线程应用,目前不需要多线程,这样代码会更简单。所有的运行时工作都在主循环中完成。所以如果 runner 或 watcher 需要做自己的事情(比如定时工作或 socker 数据接收等),则它们必须在主循环的框架中自己实现。
link-watcher
Link 监测器实现链路状态检测,可使用不同的方法检测某个端口是否有报文传输能力,即判断端口是否 Up。
目前实现的方式有:
ethtool,使用 libteam lib 获取端口 ethtool 状态变化
arp_ping,通过某端口发送 ARP 请求,如果有收到 ARP 请求,则认为链路为 up 状态。目标 IP 地址、发送时间间隔和其他选项都可以在 teamd 中配置。
nsna_ping,类似 arp_ping,但是使用 IPv6 邻居请求(NS,neighbor solicitation)和邻居发现机制(NA,neighbor advertisement)。用于纯 IPv6 环境。
可全局配置,亦可每端口配置 link-watch。用户也可以为一次配置多个 link-watcher,只有当所有的 link-watcher 报告的状态都为 up,链路才是 up。
runner
Runner 决定 Team 设备的行为。他们使用想要的内核 team 模式进行操作。Runner 监测端口 link 状态变化(使用所选择的 link-watch 监测结果),并进行相应的操作。Runner 可能还实现其他功能。
有以下 Runners 可使用(Team softdev Linux 驱动模式见以下括号):
broadcast (broadcast),几乎没做啥,只是将 teamdev 的模式置为 broadcast 模式。
roundrobin (roundrobin),几乎没做啥,只是将 teamdev 的模式置为 roundrobin 模式。
random (random),几乎没做啥,只是将 teamdev 的模式置为 random 模式。
activebackup (broadcast),监测链路变化,并选择 active 端口做报文传输。每个端口可配置自己的优先级,以及是否 sticky。sticky 的含义为即使有更高优先级的端口 Link,该端口也不会被停用。
loadbalance (loadbalance),为了做被动的负载平衡,runner 只设置 BPF 散列函数,它将确定 skb 传输的端口。为了执行主动负载平衡,runner 将不同哈希值映射到不同的以达到完美平衡。lb_hash_stats 数组选项用于获取统计信息。lb_tx_hash_to_port_mapping 数组选项用于将散列映射到 TX 端口。
lacp (loadbalance),实现 802.3ad LACP 协议。可使用 hash 或 loadbalance runner。
teamd control API
Teamd 提供 control API 供用户控制。通过 D-Bus 和 Unix socket 实现。
teamd 启动时默认使用 Unix domain socket API,如果有带 -D 选项,则使用 D-Bus API,创建 D-Bus 服务 org.libteam.teamd.[teamdevname]。
支持以下方法:
ConfigDump(),返回 teamd 所有 JSON 配置。
ConfigDumpActual(),返回所有 teamd JSON 配置,但是只包含在线端口的配置,过滤所有非在线端口。
StateDump(),返回 teamd 的状态以及其 JSON 中的子配置。
PortAdd(String port_devname),添加端口到 teamdev。
PortRemove
PortConfigUpdate
PortConfigDump
StateItemValueGet(String state_item_path),在 state 树中查找 state 条目,并返回其值。
StateItemValueSet(String state_item_path, String value)
有计划在将来用更多的方法扩展这个接口。
还有一个想法是扩展 API,以便能够将一个 runner 作为一个外部应用程序通过 control API 与 teamd 通信。
teamdctl
teamdctl 提供 control API 的封装,用来运行时监控和配置 teamd。1:1 封装 API。
teamdctl 命令更详细的描述和命令行参数,详见 manpage (man 8 teamdctl)。
Config
teamd 使用 JSON 配置文件配置,通过命令行或 .JSON 格式的的文件传递给 teamd。
选择 JSON 格式的原因是它可以轻松指定(和解析)分层配置。
teamd 配置样例(teamd1.conf):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31{
"device": "team0",
"hwaddr": "10:22:33:44:55:66",
"runner": {"name": "activebackup"},
"link_watch": {
"name": "nsna_ping",
"interval": 200,
"missed_max": 15,
"target_host": "fe80::210:18ff:feaa:bbcc"
},
"ports": {
"eth0": {
"prio": -10,
"sticky": true
},
"eth1": {
"prio": 100,
"link_watch": {"name": "ethtool"}
},
"eth2": {
"link_watch": {
"name": "arp_ping",
"interval": 100,
"missed_max": 30,
"source_host": "192.168.23.2",
"target_host": "192.168.23.1"
}
},
"eth3": {}
}
}
配置几乎不言自明。只有 link_watch 部分可能看起来有点混乱。所以在这个例子中,默认 link-watcher 是 nsna_ping,设置为每 200 毫秒发送 NAs(邻居通告)。丢失答复的最大数量为 15 个。如果丢失更多答复,link 将被视为关闭。 端口 eth1 和 eth2 指定他们自己的 link-watcher。
另一个 teamd 配置样例(teamd2.conf):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11{
"device": "team0",
"runner": {
"name": "lacp",
"active": true,
"fast_rate": true,
"tx_hash": ["eth", "ipv4", "ipv6"]
},
"link_watch": {"name": "ethtool"},
"ports": {"eth1": {}, "eth2": {}}
}
在这个样例中,tx_hash 一节值得一提。它指明使用 skb 哪些部分计算 hash。
更多详细内容见 manpage(man 8 teamd.conf)。
样例1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82# ip link
1: lo: mtu 16436 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN modeDEFAULT
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: eth0: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP modeDEFAULTqlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:b2:a7:f1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: eth3: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN modeDEFAULTqlen 1000
link/ether 00:07:e9:11:22:33 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
4: eth1: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN modeDEFAULTqlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:3d:c7:6d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: eth2: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN modeDEFAULTqlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:73:15:c2 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
# ip addr
1: lo: mtu 16436 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:b2:a7:f1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.122.182/24 brd 192.168.122.255 scope global eth0
inet6 fe80::5054:ff:feb2:a7f1/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: eth3: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN qlen 1000
link/ether 00:07:e9:11:22:33 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
4: eth1: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN qlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:3d:c7:6d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: eth2: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN qlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:73:15:c2 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
# teamd -f teamd2.conf -d
# ip link
1: lo: mtu 16436 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN modeDEFAULT
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: eth0: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP modeDEFAULTqlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:b2:a7:f1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: eth3: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN modeDEFAULTqlen 1000
link/ether 00:07:e9:11:22:33 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
4: eth1: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master team0 state UP modeDEFAULTqlen 1000
link/ether fa:29:06:7a:81:b8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: eth2: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master team0 state UP modeDEFAULTqlen 1000
link/ether fa:29:06:7a:81:b8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
6: team0: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN modeDEFAULT
link/ether fa:29:06:7a:81:b8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
# tail /var/log/messages
May 24 10:56:02 test1 kernel: [ 36.351762] team0:Portdevice eth1 added
May 24 10:56:02 test1 kernel: [ 36.357303] 8139cp 0000:00:08.0: eth2: link up, 100Mbps, full-duplex, lpa 0x05E1
May 24 10:56:02 test1 kernel: [ 36.359975] team0:Portdevice eth2 added
May 24 10:56:02 test1 teamd[883]: 0.1 sucessfully started.
May 24 10:56:03 test1 teamd[883]: eth1: Using link_watch "ethtool".
May 24 10:56:03 test1 teamd[883]: eth1: Changedportstate: "disabled" -> "expired"
May 24 10:56:03 test1 teamd[883]: eth2: Using link_watch "ethtool".
May 24 10:56:03 test1 teamd[883]: eth2: Changedportstate: "disabled" -> "expired"
May 24 10:56:03 test1 teamd[883]: eth1: Changedportstate: "expired" -> "current"
May 24 10:56:03 test1 teamd[883]: eth2: Changedportstate: "expired" -> "current"
# ip addr add 192.168.24.2/24 dev team0
# ping 192.168.24.1 -c 10 -i0.1
PING 192.168.24.1 (192.168.24.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.24.1: icmp_req=1 ttl=64 time=0.511 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.24.1: icmp_req=2 ttl=64 time=0.862 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.24.1: icmp_req=3 ttl=64 time=0.927 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.24.1: icmp_req=4 ttl=64 time=0.917 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.24.1: icmp_req=5 ttl=64 time=0.966 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.24.1: icmp_req=6 ttl=64 time=0.829 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.24.1: icmp_req=7 ttl=64 time=0.916 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.24.1: icmp_req=8 ttl=64 time=0.861 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.24.1: icmp_req=9 ttl=64 time=0.866 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.24.1: icmp_req=10 ttl=64 time=0.884 ms
--- 192.168.24.1pingstatistics ---
10 packets transmitted, 10 received, 0% packet loss, time 910ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.511/0.853/0.966/0.126 ms
# teamd -f teamd2.conf -k
# ip link
1: lo: mtu 16436 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN modeDEFAULT
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: eth0: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP modeDEFAULTqlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:b2:a7:f1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: eth3: mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN modeDEFAULTqlen 1000
link/ether 00:07:e9:11:22:33 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
4: eth1: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state DOWN modeDEFAULTqlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:3d:c7:6d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
5: eth2: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state DOWN modeDEFAULTqlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:73:15:c2 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
Bonding v.s. team features
来源: https://github.com/jpirko/libteam/wiki/Bonding-vs.-Team-features
Feature Bonding Team
broadcast TX policy
Yes
Yes
round-robin TX policy
Yes
Yes
active-backup TX policy
Yes
Yes
LACP (802.3ad) support
Yes
Yes
Hash-based TX policy
Yes
Yes
Highly customizable hash function setup No
Yes
TX load-balancing support (TLB)
Yes
Yes
RX load-balancing support (ALB)
Yes
Planned
RX load-balancing support (ALB) in bridge or openvswitch No Planned
LACP hash port select
Yes
Yes
load-balancing for LACP support No
Yes
Ethtool link monitoring
Yes
Yes
ARP link monitoring
Yes
Yes
NS/NA (IPV6) link monitoring No
Yes
ports up/down delays
Yes
Yes
port priorities and stickiness (“primary” option enhancement) No
Yes
separate per-port link monitoring setup No
Yes
multiple link monitoring setup Limited
Yes
lockless TX/RX path No(rwlock)
Yes
(RCU)
VLAN support
Yes
Yes
user-space runtime control Limited Full
Logic in user-space No
Yes
Extensibility Hard Easy
Modular design No
Yes
Performance overhead Low Very Low
D-Bus interface No
Yes
ØMQ interface No
Yes
multiple device stacking
Yes
Yes
zero config using LLDP No Planned
man
man teamd1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79js@js-vbox:~/sonic-buildimage/src/sonic-swss$ man teamd
TEAMD(8) Team daemon TEAMD(8)
NAME
teamd — team network device control daemon
SYNOPSIS
teamd -k [-p pid_file] [-g]
teamd -e [-p pid_file] [-g]
teamd -c config_text [-p pid_file] [-gdrD] [-Z address]
teamd -f config_file [-p pid_file] [-gdrD] [-Z address]
teamd -h|-V
DESCRIPTION
teamd is a daemon to control a given team network device, during runtime, as a puppeteer controls a puppet. It uses libteam to communicate with the kernel team device instance via Netlink
sockets. The behaviour depends on the selected runner and its configuration. This daemon is part of the libteam project.
OPTIONS
-h, --help
Print help text to console and exit.
-V, --version
Print version information to console and exit.
-d, --daemonize
Daemonize after startup.
-k, --kill
Kill running daemon instance.
-e, --check
Return 0 if a daemon is already running.
-f filename, --config-file filename
Load the specified configuration file.
-c text, --config text
Use given JSON format configuration string. If this option is present then -f option will be ignored.
-p filename, --pid-file filename
Use the specified PID file.
-g, --debug
Turns on debugging messages. Repeating the option increases verbosity.
-r, --force-recreate
Force team device recreation in case it already exists.
-o, --take-over
Take over the device if it already exists.
-N, --no-quit-destroy
This option also ensures that the team device is not removed after teamd finishes.
-t devicename, --team-dev devicename
Use the specified team device name (overrides "device" key in the configuration).
-n, --no-ports
Start without ports, even if they are listed in the configuration.
-D, --dbus-enable
Enable D-Bus interface.
-Z address, --zmq-enable address
Enable ZMQ interface. Possible address formats are "tcp://ip:port", "ipc://path" and others. Detailed description of ZMQ library is in page http://zguide.zeromq.org/page:all.
-U, --usock-enable
Enable UNIX domain socket interface. This is enabled by default.
-u, --usock-disable
Disable UNIX domain socket interface.
SEE ALSO
teamdctl(8), teamd.conf(5), teamnl(8), bond2team(1)
AUTHOR
Jiri Pirko is the original author and current maintainer of libteam.
libteam 2013-07-10 TEAMD(8)
man teamd.conf1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397js@js-vbox:~/sonic-buildimage/src/sonic-swss$ man teamd.conf
TEAMD.CONF(5) Team daemon configuration TEAMD.CONF(5)
NAME
teamd.conf — libteam daemon configuration file
DESCRIPTION
teamd uses JSON format configuration.
OPTIONS
device (string)
Desired name of new team device.
debug_level (int)
Level of debug messages. The higher it is the more debug messages will be printed. It is the same as adding "-g" command line options.
Default: 0 (disabled)
hwaddr (string)
Desiredhardware addressof new team device. Usual MACaddressformat is accepted.
runner.name (string)
Name of team device. The following runners are available:
broadcast —Simplerunner which directs the team device to transmit packets via all ports.
roundrobin —Simplerunner which directs the team device to transmits packets in a round-robin fashion.
activebackup — Watches for link changes and selects activeportto be used for data transfers.
loadbalance — To do passive load balancing, runner only sets up BPF hash function which will determineportfor packet transmit. To do active load balancing, runner moves hashes
among available ports trying to reach perfect balance.
lacp — Implements 802.3ad LACP protocol. Can use same Txportselection possibilities as loadbalance runner.
notify_peers.count (int)
Number of bursts of unsolicited NAs and gratuitous ARP packets sent afterportis enabled or disabled.
Default: 0 (disabled)
Defaultfor activebackup runner: 1
notify_peers.interval (int)
Value is positive number in milliseconds. Specifies an interval between bursts of notify-peer packets.
Default: 0
mcast_rejoin.count (int)
Number of bursts of multicastgrouprejoin requests sent afterportis enabled or disabled.
Default: 0 (disabled)
Defaultfor activebackup runner: 1
mcast_rejoin.interval (int)
Value is positive number in milliseconds. Specifies an interval between bursts of multicastgrouprejoin requests.
Default: 0
link_watch.name | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.name (string)
Name of link watcher to be used. The following link watchers are available:
ethtool — Uses Libteam lib to getportethtool state changes.
arp_ping — ARP requests are sent through a port. If an ARP reply is received, the link is considered to be up.
nsna_ping — Similar to the previous, except that it usesIPv6 NeighborSolicitation /NeighborAdvertisement mechanism. This is an alternative to arp_ping and becomes handy in pure-
IPv6environments.
ports (object)
List of ports,networkdevices, to be used in a team device.
See examples for more information.
ports.PORTIFNAME.queue_id (int)
ID ofqueuewhich thisportshould be mapped to.
Default: None
ACTIVE-BACKUP RUNNER SPECIFIC OPTIONS
runner.hwaddr_policy (string)
This defines thepolicyof howhardwareaddresses of team device andportdevices should be set during the team lifetime. The following are available:
same_all — All ports will always have the samehardware addressas the associated team device.
by_active — Team device adopts thehardware addressof the currently active port. This is useful when theportdevice is not able to change itshardwareaddress.
only_active — Only the activeportadopts thehardware addressof the team device. The others have their own.
Default: same_all
ports.PORTIFNAME.prio (int)
Portpriority. The higher number means higher priority.
Default: 0
ports.PORTIFNAME.sticky (bool)
Flag which indicates if theportis sticky. If set, it means theportdoes not get unselected if anotherportwith higher priority or better parameters becomes available.
Default: false
LOAD BALANCE RUNNER SPECIFIC OPTIONS
runner.tx_hash (array)
List of fragment types (strings) which should be used for packet Tx hash computation. The following are available:
eth — Uses source and destination MAC addresses.
vlan— UsesVLANid.
ipv4 — Uses source and destination IPv4 addresses.
ipv6— Uses source and destinationIPv6addresses.
ip— Uses source and destination IPv4 andIPv6addresses.
l3 — Uses source and destination IPv4 andIPv6addresses.
tcp — Uses source and destination TCP ports.
udp — Uses source and destination UDP ports.
sctp — Uses source and destination SCTP ports.
l4 — Uses source and destination TCP and UDP and SCTP ports.
runner.tx_balancer.name (string)
Name of active Tx balancer. Active Tx balancing is disabled by default. The only value available is basic.
Default: None
runner.tx_balancer.balancing_interval (int)
In tenths of a second. Periodic interval between rebalancing.
Default: 50
LACP RUNNER SPECIFIC OPTIONS
runner.active (bool)
If active is true LACPDU frames are sent along the configured links periodically. If not, it acts as "speak when spoken to".
Default: true
runner.fast_rate (bool)
Option specifies the rate at which our link partner is asked to transmit LACPDU packets. If this is true then packets will be sent once per second. Otherwise they will be sent every
30 seconds.
runner.tx_hash (array)
Same as for load balance runner.
runner.tx_balancer.name (string)
Same as for load balance runner.
runner.tx_balancer.balancing_interval (int)
Same as for load balance runner.
runner.sys_prio (int)
Systempriority, value can be 0 – 65535.
Default: 255
runner.min_ports (int)
Specifies the minimum number of ports that must be active before asserting carrier in the master interface, value can be 1 – 255. 成员口大于等于此值时,LACP 才会 Up,否则 Carrier down。
Default: 0
runner.agg_select_policy (string)
This selects thepolicyof how the aggregators will be selected. The following are available:
lacp_prio — Aggregator with highest priority according to LACP standard will be selected. Aggregator priority is affected by per-port option lacp_prio.
lacp_prio_stable — Same as previous one, except do not replace selected aggregator if it is still usable.
bandwidth — Select aggregator with highest total bandwidth.
count — Select aggregator with highest number of ports.
port_options — Aggregator with highest priority according to per-port options prio and sticky will be selected. This means that the aggregator containing theportwith the highest
priority will be selected unless at least one of the ports in the currently selected aggregator is sticky.
Default: lacp_prio
ports.PORTIFNAME.lacp_prio (int)
Portpriority according to LACP standard. The lower number means higher priority.
ports.PORTIFNAME.lacp_key (int)
Portkey according to LACP standard. It is only possible to aggregate ports with the same key.
Default: 0
ETHTOOL LINK WATCH SPECIFIC OPTIONS
link_watch.delay_up | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.delay_up (int)
Value is a positive number in milliseconds. It is the delay between the link coming up and the runner being notified about it.
Default: 0
link_watch.delay_down | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.delay_down (int)
Value is a positive number in milliseconds. It is the delay between the link going down and the runner being notified about it.
Default: 0
ARPPINGLINK WATCH SPECIFIC OPTIONS
link_watch.interval | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.interval (int)
Value is a positive number in milliseconds. It is the interval between ARP requests being sent.
link_watch.init_wait | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.init_wait (int)
Value is a positive number in milliseconds. It is the delay between link watch initialization and the first ARP request being sent.
Default: 0
link_watch.missed_max | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.missed_max (int)
Maximum number of missed ARP replies. If this number is exceeded, link is reported as down.
Default: 3
link_watch.source_host | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.source_host (hostname)
Hostname to be converted toIP addresswhich will be filled into ARP request as source address.
Default: 0.0.0.0
link_watch.target_host | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.target_host (hostname)
Hostname to be converted toIP addresswhich will be filled into ARP request as destination address.
link_watch.validate_active | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.validate_active (bool)
Validate received ARP packets on active ports. If this is not set, allincomingARP packets will be considered as a good reply.
Default: false
link_watch.validate_inactive | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.validate_inactive (bool)
Validate received ARP packets on inactive ports. If this is not set, allincomingARP packets will be considered as a good reply.
Default: false
link_watch.send_always | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.send_always (bool)
By default, ARP requests are sent on active ports only. This option allows sending even on inactive ports.
Default: false
NS/NAPINGLINK WATCH SPECIFIC OPTIONS
link_watch.interval | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.interval (int)
Value is a positive number in milliseconds. It is the interval between sending NS packets.
link_watch.init_wait | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.init_wait (int)
Value is a positive number in milliseconds. It is the delay between link watch initialization and the first NS packet being sent.
link_watch.missed_max | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.missed_max (int)
Maximum number of missed NA reply packets. If this number is exceeded, link is reported as down.
Default: 3
link_watch.target_host | ports.PORTIFNAME.link_watch.target_host (hostname)
Hostname to be converted toIPv6 addresswhich will be filled into NS packet as target address.
EXAMPLES
{
"device": "team0",
"runner": {"name": "roundrobin"},
"ports": {"eth1": {}, "eth2": {}}
}
Very basic configuration.
{
"device": "team0",
"runner": {"name": "activebackup"},
"link_watch": {"name": "ethtool"},
"ports": {
"eth1": {
"prio": -10,
"sticky": true
},
"eth2": {
"prio": 100
}
}
}
This configuration uses active-backup runner with ethtool link watcher.Porteth2 has higher priority, but the sticky flag ensures that if eth1 becomes active, it stays active while the
link remains up.
{
"device": "team0",
"runner": {"name": "activebackup"},
"link_watch": {
"name": "ethtool",
"delay_up": 2500,
"delay_down": 1000
},
"ports": {
"eth1": {
"prio": -10,
"sticky": true
},
"eth2": {
"prio": 100
}
}
}
Similar to the previous one. Only difference is that link changes are not propagated to the runner immediately, but delays are applied.
{
"device": "team0",
"runner": {"name": "activebackup"},
"link_watch": {
"name": "arp_ping",
"interval": 100,
"missed_max": 30,
"target_host": "192.168.23.1"
},
"ports": {
"eth1": {
"prio": -10,
"sticky": true
},
"eth2": {
"prio": 100
}
}
}
This configuration uses ARPpinglink watch.
{
"device": "team0",
"runner": {"name": "activebackup"},
"link_watch": [
{
"name": "arp_ping",
"interval": 100,
"missed_max": 30,
"target_host": "192.168.23.1"
},
{
"name": "arp_ping",
"interval": 50,
"missed_max": 20,
"target_host": "192.168.24.1"
}
],
"ports": {
"eth1": {
"prio": -10,
"sticky": true
},
"eth2": {
"prio": 100
}
}
}
Similar to the previous one, only this time two link watchers are used at the same time.
{
"device": "team0",
"runner": {
"name": "loadbalance",
"tx_hash": ["eth", "ipv4", "ipv6"]
},
"ports": {"eth1": {}, "eth2": {}}
}
Configuration for hash-based passive Tx load balancing.
{
"device": "team0",
"runner": {
"name": "loadbalance",
"tx_hash": ["eth", "ipv4", "ipv6"],
"tx_balancer": {
"name": "basic"
}
},
"ports": {"eth1": {}, "eth2": {}}
}
Configuration for active Tx load balancing using basic load balancer.
{
"device": "team0",
"runner": {
"name": "lacp",
"active": true,
"fast_rate": true,
"tx_hash": ["eth", "ipv4", "ipv6"]
},
"link_watch": {"name": "ethtool"},
"ports": {"eth1": {}, "eth2": {}}
}
Configuration forconnectionto LACP capable counterpart.
SEE ALSO
teamd(8), teamdctl(8), teamnl(8), bond2team(1)
AUTHOR
Jiri Pirko is the original author and current maintainer of libteam.
libteam 2013-07-09 TEAMD.CONF(5)
man teamdctl1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83js@js-vbox:~/sonic-buildimage/src/sonic-swss$ man teamdctl
TEAMDCTL(8) teamd control TEAMDCTL(8)
NAME
teamdctl — team daemon control tool
SYNOPSIS
teamdctl [options] team_device command [command_args...]
teamdctl -h
DESCRIPTION
teamdctl is a tool that allows a user to interact with a running teamd instance. It defaults to using Unix Domain Sockets, but will fall back to using the D-Bus API, to ensure reliable
operation in all environments.
OPTIONS
-h, --help
Print help text to console and exit.
-v, --verbosity
Increase output verbosity.
-o, --oneline
Force output to one line if possible.
-D, --force-dbus
Force to use D-Bus interface.
-Z address, --force-zmq address
Force to use ZMQ interface. Possible address formats are "tcp://ip:port", "ipc://path" and others. Detailed description of ZMQ library is in page http://zguide.zeromq.org/page:all.
-U, --force-usock
Force to use UNIX domain socket interface. This is the default behavior.
COMMAND
config dump
Dumps teamd JSON config.
config dump noports
Dumps teamd JSON configuration without "ports" section included.
config dump actual
Dumps teamd actual JSON configuration. It includes ports which are currently present.
state dump | state
Dumps teamd JSON state document.
state view
Prints out state of teamd parsed from JSON state document.
state item get state_item_path
Finds state item in JSON state document and returns its value.
state item set state_item_path value
Finds state item in JSON state document and sets its value by value parameter. This is available only for a limited number of paths:
setup.debug_level — User can set debug level. Higher level is more verbose.
ports.PORTIFNAME.runner.aggregator.selected — This is available for lacp runner. User can manually select the aggregator.
runner.active_port — This is available for activebackup runner. User can manually select the active port.
port add portdev
Takes port device name as argument. Adds port device into team.
port remove portdev
Takes port device name as argument. Removes port device from team.
port present portdev
Takes port device name as argument. Checks if the port device is present in team.
port config update portdev portconfig-string
Takes port device name as the first argument and JSON format configuration string as the second argument. Updates port device configuration.
port config dump portdev
Takes port device name as the first argument. Dumps port device JSON configuration to standard output.
SEE ALSO
teamd(8), teamnl(8), teamd.conf(5)
AUTHOR
Jiri Pirko is the original author and current maintainer of libteam.
libteam 2013-05-24 TEAMDCTL(8)