0、背景
现状:公司各部门业务系统有各自的工作流引擎,也有cross function的业务在不同系统或OA系统流转,没有统一的去规划布局统一的BPM解决方案,近期由于一个项目引发朝着整合统一的BPM方案,特了解一下市面上比较主流的开源和收费的工作流引擎。本文主要介绍开源的工作流引擎flowable.
1、开源工作流引擎比较
开源工作流引擎是一种用于管理和自动化业务流程的软件,它可以帮助用户实现业务流程的可视化设计、流程编排、任务调度、监控和优化等功能。本文将介绍几种常见的开源工作流引擎,并进行比较。目前市场上比较主流的开源流程引擎有:Activiti、Camunda、Flowable。
1.1、Activiti
Activiti是一个轻量级的开源工作流引擎,采用Java语言开发,基于BPMN 2.0规范,支持嵌入式部署和分布式部署。Activiti提供了丰富的API和插件,支持与Java应用程序进行集成。它还提供了Web界面和REST API,可以方便地进行流程设计、部署、调度和监控。Activiti具有以下优点:
-
易用性和灵活性:Activiti提供了简单易用的流程设计器和API,支持多种流程模型和任务类型,可以满足不同场景和需求的使用。
-
可伸缩性和性能:Activiti支持嵌入式和分布式部署,可以扩展集群规模以支持更大的业务流程和更高的并发量。此外,它还提供了优化和缓存机制,可以提高性能和响应速度。
-
社区支持和生态系统:Activiti拥有庞大的社区和活跃的开发者,提供了丰富的插件和工具,可以扩展其功能和使用。例如,Activiti Explorer可以用于流程设计和管理,Camunda Modeler可以用于编辑BPMN模型,Flowable Task可以用于任务管理等。
-
安全性和可靠性:Activiti提供了可靠的安全性控制,可以对数据进行访问控制和加密,以满足不同场景和需求的安全要求。它还提供了事务管理和错误处理机制,可以保证业务流程的可靠性和稳定性。
1.2、Camunda
Camunda是一个强大的开源工作流引擎,采用Java语言开发,支持BPMN 2.0规范和CMMN规范。Camunda提供了丰富的API和插件,支持与Java应用程序进行集成。它还提供了Web界面和REST API,可以方便地进行流程设计、部署、调度和监控。Camunda具有以下优点:
-
功能丰富和灵活性:Camunda提供了丰富的功能和灵活的流程设计,支持多种流程模型和任务类型,可以满足不同场景和需求的使用。
-
可伸缩性和性能:Camunda支持嵌入式和分布式部署,可以扩展集群规模以支持更大的业务流程和更高的并发量。此外,它还提供了优化和缓存机制,可以提高性能和响应速度。
-
社区支持和生态系统:Camunda拥有庞大的社区和活跃的开发者,提供了丰富的插件和工具,可以扩展其功能和使用。例如,Camunda Modeler可以用于编辑BPMN模型,Camunda Cockpit可以用于任务管理和流程监控,Camunda Tasklist可以用于任务列表等。
-
可扩展的架构和API:Camunda采用可扩展的架构和API,可以方便地进行集成和扩展。例如,它支持自定义流程引擎插件、外部任务处理器、表单引擎等。
-
安全性和可靠性:Camunda提供了可靠的安全性控制,可以对数据进行访问控制和加密,以满足不同场景和需求的安全要求。它还提供了事务管理和错误处理机制,可以保证业务流程的可靠性和稳定性。
1.3、Flowable
Flowable是一个开源的轻量级工作流引擎,基于Activiti 5.x版本开发,支持BPMN 2.0规范和CMMN规范。Flowable提供了丰富的API和插件,支持与Java应用程序进行集成。它还提供了Web界面和REST API,可以方便地进行流程设计、部署、调度和监控。Flowable具有以下优点:
-
易用性和灵活性:Flowable提供了简单易用的流程设计器和API,支持多种流程模型和任务类型,可以满足不同场景和需求的使用。
-
可伸缩性和性能:Flowable支持嵌入式和分布式部署,可以扩展集群规模以支持更大的业务流程和更高的并发量。此外,它还提供了优化和缓存机制,可以提高性能和响应速度。
-
社区支持和生态系统:Flowable拥有庞大的社区和活跃的开发者,提供了丰富的插件和工具,可以扩展其功能和使用。例如,Flowable Modeler可以用于流程设计和管理,Flowable Task可以用于任务管理和流程监控,Flowable Admin可以用于集群管理等。
-
可扩展的架构和API:Flowable采用可扩展的架构和API,可以方便地进行集成和扩展。例如,它支持自定义流程引擎插件、外部任务处理器、表单引擎等。
-
安全性和可靠性:Flowable提供了可靠的安全性控制,可以对数据进行访问控制和加密,以满足不同场景和需求的安全要求。它还提供了事务管理和错误处理机制,可以保证业务流程的可靠性和稳定性。
2、flowable安装
2.1、下载软件
Github链接,目前flowable已经更新到Flowable 7.0.0.M2版本了。

安装方式有很多,可以通过下载zip包也可以通过docker拉取镜像进行部署,本文采用zip的window环境部署。
下载安装包,我下载的是flowable-6.7.0版本,同时需要配合tomcat(选择的是apache-tomcat-9.0.79版本)服务进行部署,tomcat下载地址:


下载上面两个软件之后还需要配置flowale的配置数据存储,我选择的mysql数据库,当然他还支持其他数据库类型。mysql数据库是docker镜像运行的,这里不再赘述安装过程,可以看我往期docker mysql安装.
2.2、解压运行
分别解压tomcat和flowable:

把flowable-6.7.0\wars目录下的flowable-ui.war拷贝到apache-tomcat-9.0.79\webapps下面启动tomcat startup.bat
 此时会解压war文件,同时会删除war文件,同时会生成新文件apache-tomcat-9.0.79\webapps\flowable-ui.
此时会解压war文件,同时会删除war文件,同时会生成新文件apache-tomcat-9.0.79\webapps\flowable-ui.
2.3、配置数据源
修改apache-tomcat-9.0.79\webapps\flowable-ui\WEB-INF\classes\flowable-default.properties
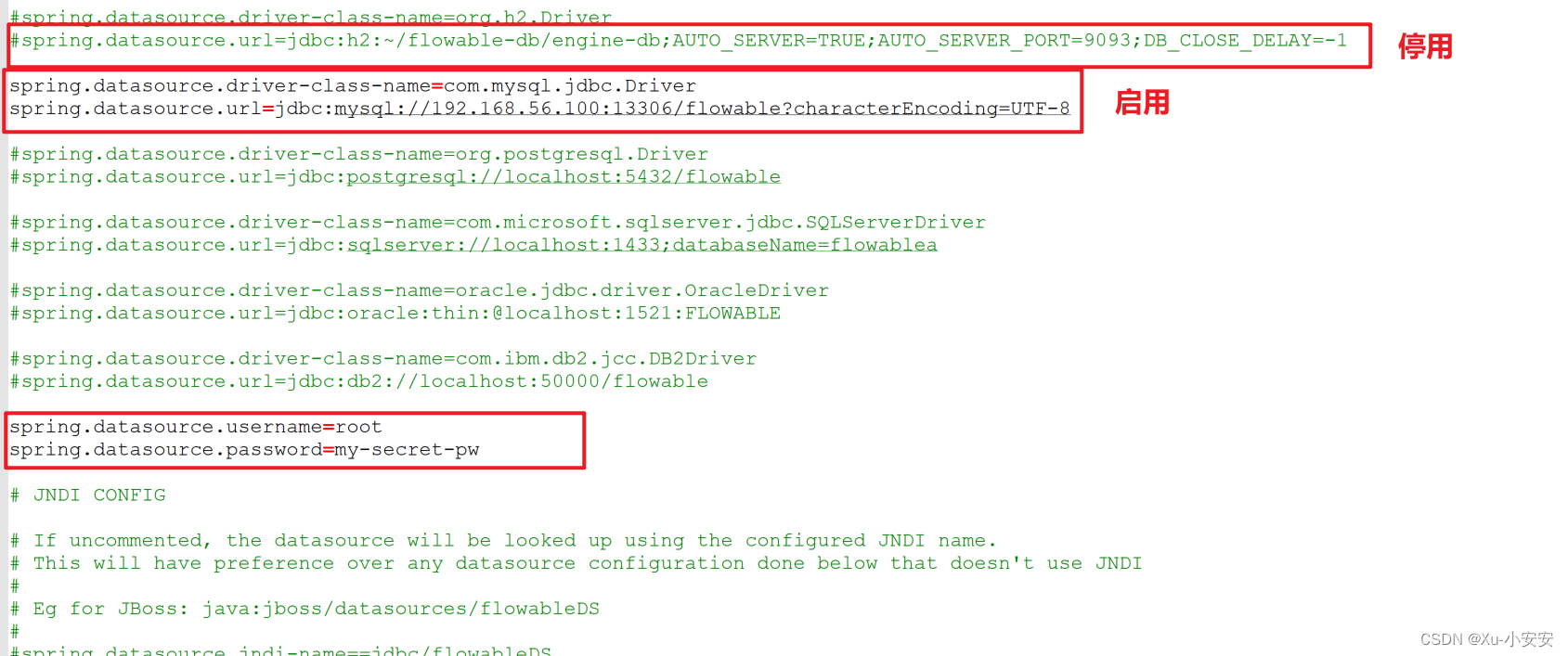
参考:
server.port=8080
server.servlet.context-path=/flowable-ui
spring.jmx.unique-names=true
# This is needed to force use of JDK proxies instead of using CGLIB
spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false
spring.aop.auto=false
spring.application.name=flowable-ui
spring.banner.location=classpath:/org/flowable/spring/boot/flowable-banner.txt
# The default domain for generating ObjectNames must be specified. Otherwise when multiple Spring Boot applications start in the same servlet container
# all would be created with the same name (com.zaxxer.hikari:name=dataSource,type=HikariDataSource) for example
spring.jmx.default-domain=${spring.application.name}
#
# SECURITY
#
spring.security.filter.dispatcher-types=REQUEST,FORWARD,ASYNC
# Expose all actuator endpoints to the web
# They are exposed, but only authenticated users can see /info and /health abd users with access-admin can see the others
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
# Full health details should only be displayed when a user is authorized
management.endpoint.health.show-details=when_authorized
# Only users with role access-admin can access full health details
management.endpoint.health.roles=access-admin
# Spring prefixes the roles with ROLE_. However, Flowable does not have that concept yet, so we need to override that with an empty string
flowable.common.app.role-prefix=
#
# SECURITY OAuth2
# Examples are for Keycloak
#
#spring.security.oauth2.resourceserver.jwt.issuer-uri=<keycloakLocation>/auth/realms/<realmName>
#spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.keycloak.client-id=<clientId>
#spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.keycloak.client-secret=<clientSecret>
#spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.keycloak.client-name=Flowable UI Keycloak
#spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.keycloak.authorization-grant-type=authorization_code
#spring.security.oauth2.client.provider.keycloak.issuer-uri=<keycloakLocation>/auth/realms/<realmName>
#spring.security.oauth2.client.provider.keycloak.user-name-attribute=preferred_username
#flowable.common.app.security.type=oauth2
#flowable.common.app.security.oauth2.authorities-attribute=groups
#flowable.common.app.security.oauth2.groups-attribute=userGroups
#flowable.common.app.security.oauth2.default-authorities=access-task
#flowable.common.app.security.oauth2.default-groups=flowableUser
#flowable.common.app.security.oauth2.full-name-attribute=name
#flowable.common.app.security.oauth2.email-attribute=email
#
# DATABASE
#
#spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.h2.Driver
#spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:~/flowable-db/engine-db;AUTO_SERVER=TRUE;AUTO_SERVER_PORT=9093;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.56.100:13306/flowable?characterEncoding=UTF-8
#spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
#spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/flowable
#spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
#spring.datasource.url=jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433;databaseName=flowablea
#spring.datasource.driver-class-name=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
#spring.datasource.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:FLOWABLE
#spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2Driver
#spring.datasource.url=jdbc:db2://localhost:50000/flowable
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=my-secret-pw
# JNDI CONFIG
# If uncommented, the datasource will be looked up using the configured JNDI name.
# This will have preference over any datasource configuration done below that doesn't use JNDI
#
# Eg for JBoss: java:jboss/datasources/flowableDS
#
#spring.datasource.jndi-name==jdbc/flowableDS
# Set whether the lookup occurs in a J2EE container, i.e. if the prefix "java:comp/env/" needs to be added if the JNDI
# name doesn't already contain it. Default is "true".
#datasource.jndi.resourceRef=true
#
# Connection pool (see https://github.com/brettwooldridge/HikariCP#configuration-knobs-baby)
#
spring.datasource.hikari.poolName=${spring.application.name}
# 10 minutes
spring.datasource.hikari.maxLifetime=600000
# 5 minutes
spring.datasource.hikari.idleTimeout=300000
spring.datasource.hikari.minimumIdle=10
spring.datasource.hikari.maximumPoolSize=50
# test query for H2, MySQL, PostgreSQL and Microsoft SQL Server
#spring.datasource.hikari.connection-test-query=select 1
# test query for Oracle
#spring.datasource.hikari.connection-test-query=SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
# test query for DB2
#spring.datasource.hikari.connection-test-query=SELECT current date FROM sysibm.sysdummy1
#
# Default Task Executor (will be used for @Async)
#
spring.task.execution.pool.core-size=2
spring.task.execution.pool.max-size=50
spring.task.execution.pool.queue-capacity=10000
spring.task.execution.thread-name-prefix=flowable-ui-task-Executor-
#
# Task scheduling
#
spring.task.scheduling.pool.size=5
#
# EMAIL
#
#flowable.mail.server.host=localhost
#flowable.mail.server.port=1025
#flowable.mail.server.username=
#flowable.mail.server.password=
#
# FLOWABLE
#
flowable.process.definition-cache-limit=512
#flowable.dmn.strict-mode=false
flowable.process.async.executor.default-async-job-acquire-wait-time=PT5S
flowable.process.async.executor.default-timer-job-acquire-wait-time=PT5S
flowable.cmmn.async.executor.default-async-job-acquire-wait-time=PT5S
flowable.cmmn.async.executor.default-timer-job-acquire-wait-time=PT5S
# The maximum file upload limit. Set to -1 to set to 'no limit'. Expressed in bytes
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=10MB
# The maximum request size limit. Set to -1 to set to 'no limit'.
# When multiple files can be uploaded this needs to be more than the 'max-file-size'.
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=10MB
# For development purposes, data folder is created inside the sources ./data folder
flowable.content.storage.root-folder=data/
flowable.content.storage.create-root=true
flowable.common.app.idm-admin.user=admin
flowable.common.app.idm-admin.password=test
flowable.experimental.debugger.enabled=false
# Rest API in task application
# If false, disables the rest api in the task app
flowable.task.app.rest-enabled=true
# Configures the way user credentials are verified when doing a REST API call:
# 'any-user' : the user needs to exist and the password need to match. Any user is allowed to do the call (this is the pre 6.3.0 behavior)
# 'verify-privilege' : the user needs to exist, the password needs to match and the user needs to have the 'rest-api' privilege
# If nothing set, defaults to 'verify-privilege'
flowable.rest.app.authentication-mode=verify-privilege
# Enable form field validation after form submission on the engine side
flowable.form-field-validation-enabled=false
# Flowable Admin Properties
# Passwords for rest endpoints and master configs are stored encrypted in the database using AES/CBC/PKCS5PADDING
# It needs a 128-bit initialization vector (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Initialization_vector)
# and a 128-bit secret key represented as 16 ascii characters below
#
# Do note that if these properties are changed after passwords have been saved, all existing passwords
# will not be able to be decrypted and the password would need to be reset in the UI.
flowable.admin.app.security.encryption.credentials-i-v-spec=j8kdO2hejA9lKmm6
flowable.admin.app.security.encryption.credentials-secret-spec=9FGl73ngxcOoJvmL
#flowable.admin.app.security.preemptive-basic-authentication=true
# Flowable IDM Properties
#
# LDAP
#
#flowable.idm.ldap.enabled=true
#flowable.idm.ldap.server=ldap://localhost
#flowable.idm.ldap.port=10389
#flowable.idm.ldap.user=uid=admin, ou=system
#flowable.idm.ldap.password=secret
#flowable.idm.ldap.base-dn=o=flowable
#flowable.idm.ldap.query.user-by-id=(&(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)(uid={0}))
#flowable.idm.ldap.query.user-by-full-name-like=(&(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)(|({0}=*{1}*)({2}=*{3}*)))
#flowable.idm.ldap.query.all-users=(objectClass=inetOrgPerson)
#flowable.idm.ldap.query.groups-for-user=(&(objectClass=groupOfUniqueNames)(uniqueMember={0}))
#flowable.idm.ldap.query.all-groups=(objectClass=groupOfUniqueNames)
#flowable.idm.ldap.query.group-by-id=(&(objectClass=groupOfUniqueNames)(uniqueId={0}))
#flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.user-id=uid
#flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.first-name=cn
#flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.last-name=sn
#flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.email=mail
#flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.group-id=cn
#flowable.idm.ldap.attribute.group-name=cn
#flowable.idm.ldap.cache.group-size=10000
#flowable.idm.ldap.cache.group-expiration=180000
#
# Keycloak
#
#flowable.idm.app.keycloak.enabled=true
#flowable.idm.app.keycloak.server=<keycloakLocation>
#flowable.idm.app.keycloak.authentication-realm=master
#flowable.idm.app.keycloak.authentication-user=admin
#flowable.idm.app.keycloak.authentication-password=admin
#flowable.idm.app.keycloak.realm=<realm>
#
# DEFAULT ADMINISTRATOR ACCOUNT
#
flowable.idm.app.admin.user-id=admin
flowable.idm.app.admin.password=test
flowable.idm.app.admin.first-name=Test
flowable.idm.app.admin.last-name=Administrator
flowable.idm.app.admin.email=test-admin@example-domain.tld
# Enable and configure JMS
#flowable.task.app.jms-enabled=true
#spring.activemq.broker-url=tcp://localhost:61616
# Enable and configure RabbitMQ
#flowable.task.app.rabbit-enabled=true
#spring.rabbitmq.addresses=localhost:5672
#spring.rabbitmq.username=guest
#spring.rabbitmq.password=guest
# Enable and configure Kafka
#flowable.task.app.kafka-enabled=true
#spring.kafka.bootstrap-servers=localhost:9092
默认情况下flowable有没有把mysql驱动程序打入到war包里面,需要手动添加对应的驱动。apache-tomcat-9.0.79\webapps\flowable-ui\WEB-INF\lib 我选择的是mysql-connector-java-5.1.45.jar驱动,具体可以从网上下载也可以通过maven方式从中央仓库拉取。

再次启动tomcat,访问http://127.0.0.1:8080/flowable-ui 初始用户名和密码:admin/test
3、springboot接入flowable
登录flowable之后选择建模器应用程序,添加一个流程,我这边已经添加了一个简单的请假流程。


新入门可以导入我们流程定义,具体文件在看的我资源。重点介绍springboot如何集成flowable,配置后续有机会在单独介绍里程配置说明。
新建springboot项目添加响应的依赖。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flowable</groupId>
<artifactId>flowable-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>6.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.45</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Flowable 内部日志采用 SLF4J -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>

application.yml配置:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.56.100:13306/flowable?useSSL=false&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: my-secret-pw
# flowable 配置
flowable:
# 关闭异步,不关闭历史数据的插入就是异步的,会在同一个事物里面,无法回滚
# 开发可开启会提高些效率,上线需要关闭
async-executor-activate: false
server:
port: 18080
Controller
import liquibase.pro.packaged.O;
import liquibase.pro.packaged.U;
import org.flowable.bpmn.model.BpmnModel;
import org.flowable.engine.*;
import org.flowable.engine.history.HistoricActivityInstance;
import org.flowable.engine.history.HistoricProcessInstance;
import org.flowable.engine.runtime.ActivityInstance;
import org.flowable.engine.runtime.Execution;
import org.flowable.engine.runtime.ProcessInstance;
import org.flowable.image.ProcessDiagramGenerator;
import org.flowable.task.api.Task;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author pyj
* @date 2019/10/30
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("flowable")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private RuntimeService runtimeService;
@Autowired
private TaskService taskService;
@Autowired
private HistoryService historyService;
@Autowired
private RepositoryService repositoryService;
@Autowired
private ProcessEngine processEngine;
/**
* 创建流程
*
* @param userId
* @param days
* @param reason
* @return
*/
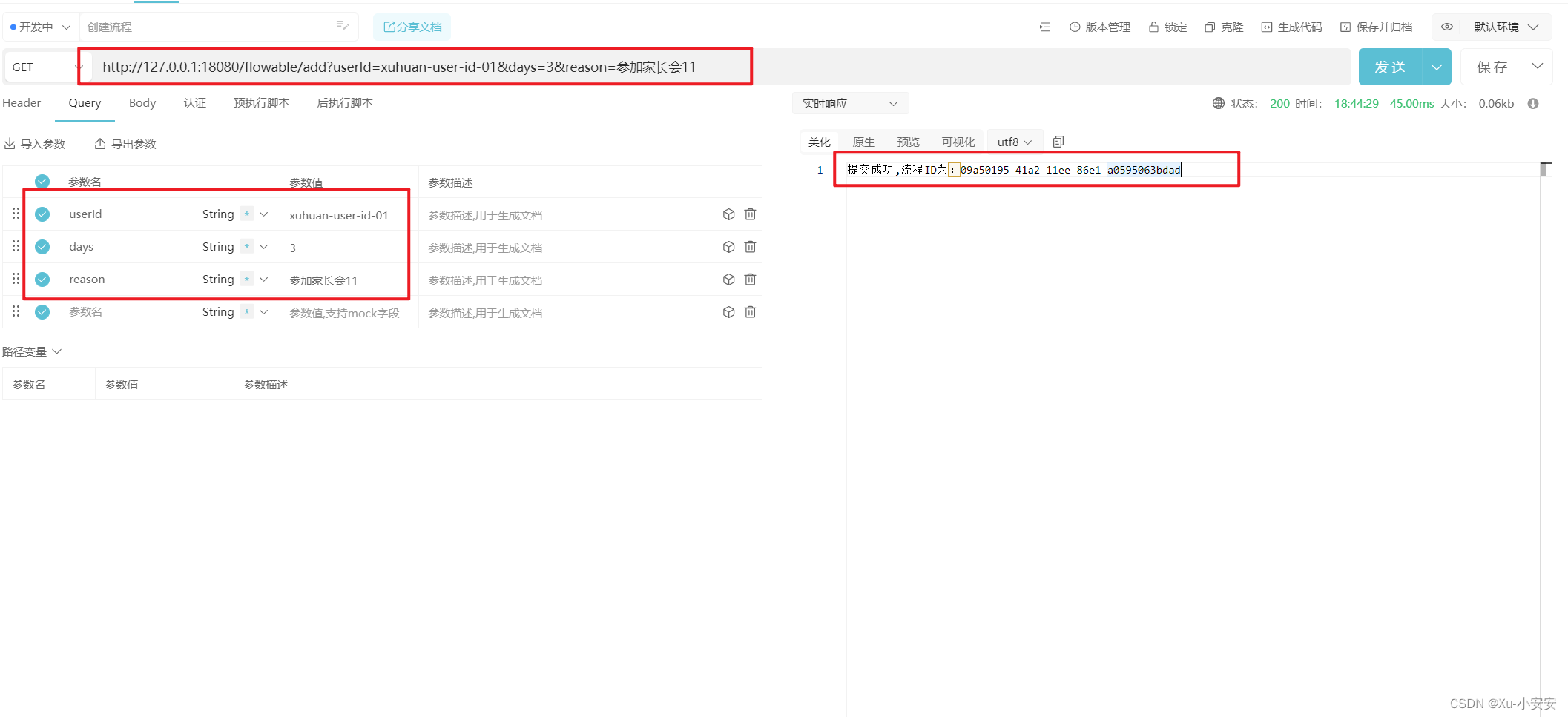
@GetMapping("add")
public String addExpense(String userId, String days, String reason) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("employee", userId);
map.put("nrOfHolidays", days);
map.put("description", reason);
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("holidayRequest", map);
return "提交成功,流程ID为:" + processInstance.getId();
}
/**
* 获取指定用户组流程任务列表
*
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("listtask")
public Object listtask() {
StringBuffer btf = new StringBuffer();
List<Task> list = taskService.createTaskQuery().list();
for (Task task : list){
btf.append(task.getId()+"\r\n");
System.out.println(task.getId());
}
return btf.toString();
}
/**
* 获取指定用户组流程任务列表
*
* @param group
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("list")
public Object list(String group) {
List<Task> list = taskService.createTaskQuery().list();
List<Task> tasks = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskCandidateGroup(group).list();
return tasks.toString();
}
/**
* 通过/拒绝任务
*
* @param taskId
* @param approved 1 :true 2:false
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("apply")
public String apply(String taskId, String approved) {
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId).singleResult();
if (task == null) {
return "流程不存在";
}
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<>();
Boolean apply = approved.equals("1") ? true : false;
variables.put("approved", apply);
taskService.complete(taskId, variables);
return "审批是否通过:" + approved;
}
/**
* 查看历史流程记录
*
* @param processInstanceId
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("historyList")
public Object getHistoryList(String processInstanceId) {
List<HistoricActivityInstance> historicActivityInstances = historyService.createHistoricActivityInstanceQuery()
.processInstanceId(processInstanceId).finished().orderByHistoricActivityInstanceEndTime().asc().list();
return historicActivityInstances;
}
/**
* 驳回流程实例
*
* @param taskId
* @param targetTaskKey
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("rollbask")
public String rollbaskTask(String taskId, String targetTaskKey) {
Task currentTask = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId).singleResult();
if (currentTask == null) {
return "节点不存在";
}
List<String> key = new ArrayList<>();
key.add(currentTask.getTaskDefinitionKey());
runtimeService.createChangeActivityStateBuilder()
.processInstanceId(currentTask.getProcessInstanceId())
.moveActivityIdsToSingleActivityId(key, targetTaskKey)
.changeState();
return "驳回成功...";
}
/**
* 终止流程实例
*
* @param processInstanceId
*/
public String deleteProcessInstanceById(String processInstanceId) {
// ""这个参数本来可以写删除原因
runtimeService.deleteProcessInstance(processInstanceId, "");
return "终止流程实例成功";
}
/**
* 挂起流程实例
*
* @param processInstanceId 当前流程实例id
*/
@GetMapping("hangUp")
public String handUpProcessInstance(String processInstanceId) {
runtimeService.suspendProcessInstanceById(processInstanceId);
return "挂起流程成功...";
}
/**
* 恢复(唤醒)被挂起的流程实例
*
* @param processInstanceId 流程实例id
*/
@GetMapping("recovery")
public String activateProcessInstance(String processInstanceId) {
runtimeService.activateProcessInstanceById(processInstanceId);
return "恢复流程成功...";
}
/**
* 判断传入流程实例在运行中是否存在
*
* @param processInstanceId
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("isExist/running")
public Boolean isExistProcIntRunning(String processInstanceId) {
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.createProcessInstanceQuery().processInstanceId(processInstanceId).singleResult();
if (processInstance == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 判断流程实例在历史记录中是否存在
* @param processInstanceId
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("isExist/history")
public Boolean isExistProcInHistory(String processInstanceId) {
HistoricProcessInstance historicProcessInstance = historyService.createHistoricProcessInstanceQuery().processInstanceId(processInstanceId).singleResult();
if (historicProcessInstance == null) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 我发起的流程实例列表
*
* @param userId
* @return 流程实例列表
*/
@GetMapping("myTasks")
public List<HistoricProcessInstance> getMyStartProcint(String userId) {
List<HistoricProcessInstance> list = historyService
.createHistoricProcessInstanceQuery()
.startedBy(userId)
.orderByProcessInstanceStartTime()
.asc()
.list();
return list;
}
/**
* 查询流程图
*
* @param httpServletResponse
* @param processId
* @throws Exception
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "processDiagram")
public void genProcessDiagram(HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, String processId) throws Exception {
List<ActivityInstance> activityInstanceList = runtimeService.createActivityInstanceQuery().list();
for(ActivityInstance activityInstance : activityInstanceList){
System.out.println(activityInstance.getId());
}
System.out.println("=========================================================================");
List<ProcessInstance> list = runtimeService.createProcessInstanceQuery().list();
for(ProcessInstance processInstance : list){
System.out.println(processInstance.getId());
}
ProcessInstance pi = runtimeService.createProcessInstanceQuery().processInstanceId(processId).singleResult();
//流程走完的不显示图
if (pi == null) {
return;
}
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().processInstanceId(pi.getId()).singleResult();
//使用流程实例ID,查询正在执行的执行对象表,返回流程实例对象
String InstanceId = task.getProcessInstanceId();
List<Execution> executions = runtimeService
.createExecutionQuery()
.processInstanceId(InstanceId)
.list();
//得到正在执行的Activity的Id
List<String> activityIds = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> flows = new ArrayList<>();
for (Execution exe : executions) {
List<String> ids = runtimeService.getActiveActivityIds(exe.getId());
activityIds.addAll(ids);
}
//获取流程图
BpmnModel bpmnModel = repositoryService.getBpmnModel(pi.getProcessDefinitionId());
ProcessEngineConfiguration engconf = processEngine.getProcessEngineConfiguration();
ProcessDiagramGenerator diagramGenerator = engconf.getProcessDiagramGenerator();
InputStream in = diagramGenerator.generateDiagram(bpmnModel, "png", activityIds, flows, engconf.getActivityFontName(), engconf.getLabelFontName(), engconf.getAnnotationFontName(), engconf.getClassLoader(), 1.0,true);
OutputStream out = null;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int legth = 0;
try {
out = httpServletResponse.getOutputStream();
while ((legth = in.read(buf)) != -1) {
out.write(buf, 0, legth);
}
} finally {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
}
Flowable提供了几个Service接口和实现类,可以通过service拿到流程的一些定义、流转等信息。
正如TestController里面定义的几个方法,分别是实例化流程,审批流程,查看流程等操作。如下
实例化流程:
审批流程:

拉取当前流程任务清单:

查看流程状态:
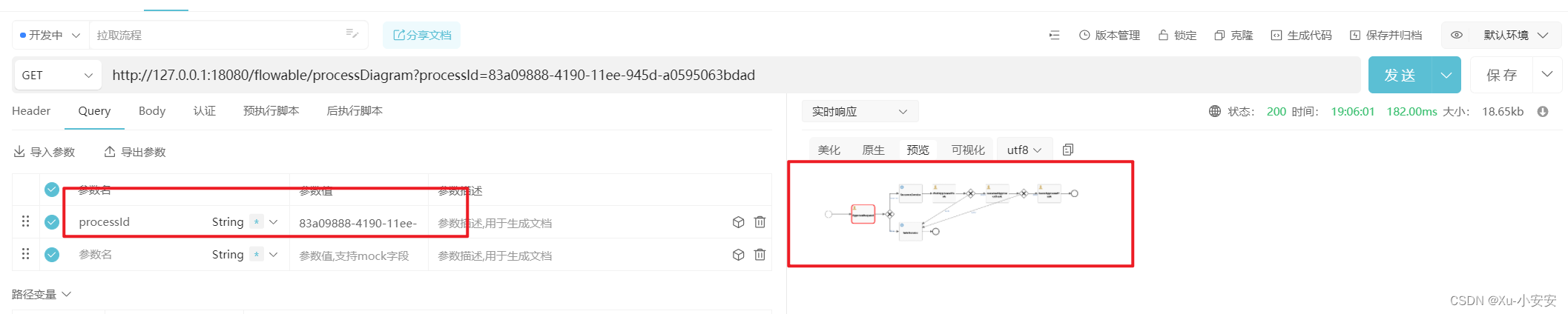
具体大家可以参考如下文章有详细的springboot集成指引。
Flowable BPMN 用户手册 (v 6.3.0)