@Author:zxw
@Email:502513206@qq.com
目录
- Sentinel源码分析(一) - 初识Sentinel
- Sentinel源码分析(二) - Entry构建
1.前言
之前已经分析过Entry的构造流程,我们知道Sentinel关于规则和流控的所有逻辑都在其内部的ProcessorSlotChain调用链路上,首先看看接口提供的方法有哪些。对于链表结构我们清楚,就是不断获取下一个节点,然后进行方法调用。这里该接口提供了两个方法分别为入口entry和出口exit。对于出口方法更多的是用来做些统计,比如断路器就可以通过出口的方法来判断是否开启。
void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, T param, int count, boolean prioritized,
Object... args) throws Throwable;
void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args);
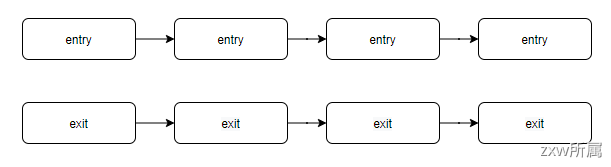
以下是Sentinel官方提供的链路调用图

这两个方法的调用逻辑也如同上图,在开始时顺着链路执行entry方法,在结束时顺着链路执行exit方法
2.源码分析
上篇文章分析过构造ProcessorSlotChain链路是通过Spi机制将其实例化的,并且会通过@Spi注解上的order字段进行排序,这里已经通过源码上的注解标识对调用顺序进行了排序
- NodeSelectorSlot:调用链路
- ClusterBuilderSlot:统计簇点
- LogSlot:日志
- StatisticSlot:统计
- AuthoritySlot:来源访问控制
- SystemSlot:系统保护
- FlowSlot:流量控制
- DegradeSlot:熔断降级
- ParamFlowSlot:热点参数限流
在代码中的结构如下

其实会发现和Sentinel官方提供的实现图还是有些细微的出入的

接下来就对链路中的节点进行分析
2.1 NodeSelectorSlot
该节点的作用就是收集资源路径,并将资源路径以树状结构存储起来,用于根据调用路径来限流降级。
DefaultNode node = map.get(context.getName());
if (node == null) {
synchronized (this) {
node = map.get(context.getName());
if (node == null) {
node = new DefaultNode(resourceWrapper, null);
HashMap<String, DefaultNode> cacheMap = new HashMap<String, DefaultNode>(map.size());
cacheMap.putAll(map);
cacheMap.put(context.getName(), node);
map = cacheMap;
((DefaultNode) context.getLastNode()).addChild(node);
}
}
}
context.setCurNode(node);
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
2.2 ClusterBuilderSlot
此插槽用于构建资源的 ClusterNode 以及调用来源节点。ClusterNode 保持资源运行统计信息(响应时间、QPS、block 数目、线程数、异常数等)以及原始调用者统计信息列表。来源调用者的名字由 ContextUtil.enter(contextName,origin) 中的 origin 标记
2.3 LogSlot
根据名字可知该节点是个日志记录节点,不过收集的是发生BlockException异常后的日志
try {
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, obj, count, prioritized, args);
} catch (BlockException e) {
EagleEyeLogUtil.log(resourceWrapper.getName(), e.getClass().getSimpleName(), e.getRuleLimitApp(),
context.getOrigin(), count);
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
RecordLog.warn("Unexpected entry exception", e);
}
2.4 StatisticSlot
该节点是个用于统计实时的调用数据。比如资源节点通过的请求数量、线程数量等等。
- clusterNode:资源唯一标识的 ClusterNode 的 runtime 统计
- origin:根据来自不同调用者的统计信息
- defaultnode: 根据上下文条目名称和资源 ID 的 runtime 统计
- 入口的统计
但是统计一般是请求结束后进行统计,所以会将调用传个下个节点,等下个节点执行完毕后在进行统计
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
node.increaseThreadNum();
node.addPassRequest(count);
if (context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode() != null) {
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().increaseThreadNum();
context.getCurEntry().getOriginNode().addPassRequest(count);
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() == EntryType.IN) {
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.increaseThreadNum();
Constants.ENTRY_NODE.addPassRequest(count);
}
for (ProcessorSlotEntryCallback<DefaultNode> handler : StatisticSlotCallbackRegistry.getEntryCallbacks()) {
handler.onPass(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, args);
}
2.5 AuthoritySlot
在该节点中,可以配置我们应用的黑白名单。在我们的Context上下文中有个origin字段来区分应用的来源,在访问就可以通过Sentinel配置应用访问黑白名单限制,以此来拒绝某些origin的访问
public class Context {
private String origin = "";
}
具体的配置通过配置规则时,配置AuthorityRule来实现
void checkBlackWhiteAuthority(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context) throws AuthorityException {
Map<String, Set<AuthorityRule>> authorityRules = AuthorityRuleManager.getAuthorityRules();
if (authorityRules == null) {
return;
}
Set<AuthorityRule> rules = authorityRules.get(resource.getName());
if (rules == null) {
return;
}
for (AuthorityRule rule : rules) {
if (!AuthorityRuleChecker.passCheck(rule, context)) {
throw new AuthorityException(context.getOrigin(), rule);
}
}
}
以下是添加授权规则的测试代码
public static void initAuthorityRule(){
List<AuthorityRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
AuthorityRule rule = new AuthorityRule();
rule.setStrategy(RuleConstant.AUTHORITY_WHITE);
rule.setResource("HelloWorld");
rule.setLimitApp("hello");
AuthorityRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
2.6 SystemSlot
该节点会根据对于当前系统的整体情况,对入口资源的调用进行动态调配。其原理是让入口的流量和当前系统的预计容量达到一个动态平衡。注意系统规则只对入口流量起作用(调用类型为 EntryType.IN)。该检查默认是关闭状态的需要手动开启,主要会在以下几个方面进行判断
- qps
- 当前线程数
- 平均响应时间
- 平均响应时间
- cpu使用率
当超过系统预期值时,会抛出SystemBlockException异常
public static void checkSystem(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) throws BlockException {
if (resourceWrapper == null) {
return;
}
if (!checkSystemStatus.get()) {
return;
}
if (resourceWrapper.getEntryType() != EntryType.IN) {
return;
}
double currentQps = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0.0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.successQps();
if (currentQps > qps) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "qps");
}
int currentThread = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.curThreadNum();
if (currentThread > maxThread) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "thread");
}
double rt = Constants.ENTRY_NODE == null ? 0 : Constants.ENTRY_NODE.avgRt();
if (rt > maxRt) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "rt");
}
if (highestSystemLoadIsSet && getCurrentSystemAvgLoad() > highestSystemLoad) {
if (!checkBbr(currentThread)) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "load");
}
}
if (highestCpuUsageIsSet && getCurrentCpuUsage() > highestCpuUsage) {
throw new SystemBlockException(resourceWrapper.getName(), "cpu");
}
}
2.7 FlowSlot
该节点主要根据预设的资源的统计信息,按照固定的次序,依次生效。如果一个资源对应两条或者多条流控规则,则会根据如下次序依次检验,直到全部通过或者有一个规则生效为止:
- 指定应用生效的规则,即针对调用方限流的;
- 调用方为 other 的规则;
- 调用方为 default 的规则。
我们在配置规则的时候,是个List列表,Sentinel则通过将所有的Rule取出然后循环遍历
public void checkFlow(Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider, ResourceWrapper resource,
Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized) throws BlockException {
if (ruleProvider == null || resource == null) {
return;
}
Collection<FlowRule> rules = ruleProvider.apply(resource.getName());
if (rules != null) {
for (FlowRule rule : rules) {
if (!canPassCheck(rule, context, node, count, prioritized)) {
throw new FlowException(rule.getLimitApp(), rule);
}
}
}
}
2.8 DegradeSlot
该节点主要针对资源的平均响应时间(RT)以及异常比率,来决定资源是否在接下来的时间被自动熔断掉。
public boolean tryPass(Context context) {
if (currentState.get() == State.CLOSED) {
return true;
}
if (currentState.get() == State.OPEN) {
return retryTimeoutArrived() && fromOpenToHalfOpen(context);
}
return false;
}
2.9 ParamFlowSlot
该节点是个热点参数流控
void checkFlow(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) throws BlockException {
if (args != null) {
if (ParamFlowRuleManager.hasRules(resourceWrapper.getName())) {
List<ParamFlowRule> rules = ParamFlowRuleManager.getRulesOfResource(resourceWrapper.getName());
Iterator var5 = rules.iterator();
ParamFlowRule rule;
do {
if (!var5.hasNext()) {
return;
}
rule = (ParamFlowRule)var5.next();
this.applyRealParamIdx(rule, args.length);
ParameterMetricStorage.initParamMetricsFor(resourceWrapper, rule);
} while(ParamFlowChecker.passCheck(resourceWrapper, rule, count, args));
String triggeredParam = "";
if (args.length > rule.getParamIdx()) {
Object value = args[rule.getParamIdx()];
triggeredParam = String.valueOf(value);
}
throw new ParamFlowException(resourceWrapper.getName(), triggeredParam, rule);
}
}
}
3.总结
目前大概对Sentinel所有框架提供的链路节点已经有了一个初步的了解,接下来就深入到节点中看具体的实现。
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系:hwhale#tublm.com(使用前将#替换为@)