Kotlin is the official programming language for Android apps development. In this tutorial, we’ll be discussing TextViews in Android applications using Kotlin programming. We’ll create and change TextViews code in Kotlin programming.
Kotlin是用于Android应用程序开发的官方编程语言。 在本教程中,我们将讨论使用Kotlin编程的Android应用程序中的TextView。 我们将在Kotlin编程中创建和更改TextViews代码。
Android TextView概述 (Android TextView Overview)
Android TextView is a subclass of the View class. The View class typically occupy our window. TextView is used to display text on the screen. We can do a lot of fancy things using TextView.
Android TextView是View类的子类。 View类通常占据我们的窗口。 TextView用于在屏幕上显示文本。 我们可以使用TextView做很多花哨的事情。
Let’s start with a fresh project in Android Studio.
让我们从Android Studio中的一个新项目开始。
Create a new project and make sure you’ve enabled Kotlin in the setup wizard.
创建一个新项目,并确保已在设置向导中启用Kotlin。
在XML布局中创建TextView (Creating TextView in XML Layout)
TextView is created in an xml layout in the following manner.
TextView以以下方式在xml布局中创建。
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello World!" />
The four attributes defined above are the core attributes of the TextView widget.
上面定义的四个属性是TextView小部件的核心属性。
- The
id property is used to set a unique identifier. It’s set as @+id/ followed by the name you assign. The same name would be used to retrieve the TextView property in our Kotlin Activity class. id属性用于设置唯一标识符。 设置为@+id/后跟您分配的名称。 在我们的Kotlin Activity类中,将使用相同的名称来检索TextView属性。 - The text property is used to set the string text to be displayed in the TextView. text属性用于设置要在TextView中显示的字符串文本。
- As it is evident from the names itself, layout_width and layout_height are used to set the boundaries of the TextView. The wrap_content means wrapping the width, height to the length of the text. The match_parent means the TextView matches the width/height of the enclosed parent view. We can also set hardcoded values in dp (device independent pixels). 从名称本身可以明显看出,layout_width和layout_height用于设置TextView的边界。 wrap_content表示将宽度,高度包装为文本的长度。 match_parent表示TextView与封闭的父视图的宽度/高度匹配。 我们还可以设置dp(与设备无关的像素)中的硬编码值。
Clean Code Tips: Instead of hardcoding the string, define it inside the strings.xml and set the text in the layout as follows.
干净的代码提示 :不用对字符串进行硬编码,而是在strings.xml内定义它,并按如下所示在布局中设置文本。
android:text="@string/app_name"
Let’s apply some attributes over the TextView in XML.
让我们在XML的TextView上应用一些属性。
TextView XML属性 (TextView XML Attributes)
Let’s give you a quick tour of some of the popular attributes of TextView widget.
让我们快速浏览一下TextView小部件的一些流行属性。
android:textSize: sets the size of the TextView. It’s recommended to use sp instead of dp. The sp stands for scale independent pixels and scales the font. Example: 16sp. android:textSize :设置TextView的大小。 建议使用sp代替dp。 sp代表与比例无关的像素并缩放字体。 示例:16sp。 - The
android:textColor is used to set a color for the text. Typically it is of the format #rgb, #rrggbb, #aarrggbb. android:textColor用于设置文本的颜色。 通常,其格式为#rgb,#rrggbb,#aarrggbb。 - The
android:background attribute is used to set the background color of the TextView. android:background属性用于设置TextView的背景颜色。 - The
android:textStyle is used to set the style among bold, italic, and normal. If you want to set bold and italic, use android:textStyle = “bold|italic”. android:textStyle用于在粗体,斜体和普通之间设置样式。 如果要设置粗体和斜体,请使用android:textStyle =“ bold | italic”。 - The
android:textAppearance attribute is used to set the style on a TextView, which includes its own color, font, and size. We can create custom styles in the styles.xml file. android:textAppearance属性用于在TextView上设置样式,该样式包括其自己的颜色,字体和大小。 我们可以在styles.xml文件中创建自定义样式。 android:visibility is used to set the visibililty of the text, possible values are visible, invisible, and gone. The gone makes the textview invisible and removes it from the current position in the layout. android:visibility用于设置文本的可见性,可能的值是visible , invisible和gone 。 gone使textview不可见,并将其从布局中的当前位置删除。 - The
android:ellipsize is used to handle situations when the length of the text exceeds the limit. android:ellipsize用于处理文本长度超过限制的情况。 -
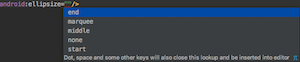
.
- The
end adds dots when the text reaches the limit width of the TextView. The start adds the dots at the beginning. The marquee is used to make the text continously slide left and right to show the full text. 当文本达到TextView的限制宽度时, end添加点。 start在start添加点。 marquee用于使文本连续左右滑动以显示全文。 - The
android:onClick is the method name in the Kotlin Activity class that’ll be invoked on TextView click. We need to ensure android:clickable is set to true for this attribute. android:onClick是Kotlin Activity类中的方法名称,它将在TextView click上调用。 我们需要确保将此属性的android:clickable设置为true。 android:typeface is used to set the typeface of the text. android:typeface用于设置文本的字体。 android:drawableLeft is used to set a drawable/mipmap image or vector asset besides the TextView. android:drawableLeft用于设置TextView之外的drawable / mipmap图像或矢量资源。 - The
android:gravity is used to set the position of the text relative to its dimensions. android:gravity用于设置文本相对于其尺寸的位置。 android:layout_margin is used to set the spacing of the TextView from the other views present in the layout. The layout_marginLeft, layout_marginRight, layout_marginTop, layout_marginBottom are used for setting margins on the individiual sides. android:layout_margin用于设置TextView与布局中其他视图的间距。 layout_marginLeft,layout_marginRight,layout_marginTop,layout_marginBottom用于在各个面上设置边距。 - The
android:padding is used to add spacing inside the four sides of the TextView. The possible values are paddingLeft, paddingRight, paddingTop, and paddingBottom. android:padding用于在TextView的四个侧面内添加间距。 可能的值为paddingLeft,paddingRight,paddingTop和paddingBottom。
Let’s use the xml attributes on a TextView in our layout.
让我们在布局中的TextView上使用xml属性。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:id="@+id/linearLayout"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="net.androidly.androidtextviewkotlin.MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textViewEllipsize"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="8dp"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:maxLines="1"
android:text="@string/long_string"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textViewClickMe"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="8dp"
android:background="@color/colorPrimaryDark"
android:padding="@android:dimen/app_icon_size"
android:shadowColor="@android:color/black"
android:text="TextView Click Me" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Android TextView Color"
android:textAllCaps="true"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
android:textColor="#234568"
android:textStyle="bold|italic" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textViewOpacity"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="16dp"
android:drawableLeft="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:drawablePadding="16dp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Android TextView Opacity is 50 percent"
android:textColor="#50234568"
android:textSize="14sp"
android:typeface="serif" />
</LinearLayout>
Note: We’ve replaced the ConstraintLayout with a LinearLayout to make things easier.
注意:我们已经使用LinearLayout替换了ConstraintLayout,使事情变得更容易。

Notice the opacity in the last TextView
注意最后一个TextView中的不透明度
For more info on XML attributes for Android TextView, visit the Google docs attached at the end of this page or JournalDev Android TextView tutorial.
有关Android TextView的XML属性的详细信息,请访问此页末尾随附的Google文档或JournalDev Android TextView教程。
In the following section, we’ll create TextView programmatically using Kotlin and set Kotlin functions, properties, and use lambda functions over the TextView.
在以下部分中,我们将使用Kotlin以编程方式创建TextView,并设置Kotlin函数,属性,并在TextView上使用lambda函数。
使用Kotlin创建Android TextView (Creating Android TextView using Kotlin)
We can get the TextView in our MainActivity.kt Kotlin class using findViewById.
我们可以使用findViewById在MainActivity.kt Kotlin类中获取TextView。
The findViewById is used to get a view from the XML in the Activity class using the id specified. It works like a dictionary – key/value pair.
findViewById用于使用指定的ID从Activity类中的XML获取视图。 它像字典一样工作-键/值对。
package net.androidly.androidtextviewkotlin
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.util.Log
import android.widget.TextView
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
val TAG = "MainActivity"
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
var textView = findViewById<textview>(R.id.textView)
//text property is equivalent to getText() or setText() in Java.
Log.d(TAG,"TextView text is ${textView.text}") //Logs TextView text is Android TextView Color
//setting the text.
textView.text = "Text changed"
//Setting the text from the strings.xml file.
textView.text = resources.getString(R.string.app_name)
}
}
Code Explanation:
代码说明 :
- MainActivity Kotlin class extends AppCompatActivity. MainActivity Kotlin类扩展了AppCompatActivity。
- We’ve created the textView property by using
findViewById
. Though from Android API > 24 you can ignore specifying the type explicitly. 我们使用findViewById创建了textView属性
。 虽然从Android API> 24开始,您可以忽略显式指定类型。 - The text property is used as getter/setter on the TextView. It returns a CharSequence. text属性用作TextView上的getter / setter方法。 它返回一个CharSequence 。
${textView.text} implcitily converts the CharSequence to a String. ${textView.text} textView.text ${textView.text}隐式地将CharSequence转换为String。 - The
text property in Kotlin is equivalent to getText() and setText(String) in Java. Kotlin中的text属性等效于Java中的getText()和setText(String) 。 - To set the string from the strings.xml file, we call
resources.getString(R.string.
)
. The resources property is equivalent to getResources() from Java. 要从strings.xml文件设置字符串,我们调用resources.getString(R.string. )
resources.getString(R.string. )
。 resources属性等效于Java中的getResources() 。
在TextView Kotlin代码中处理空值 (Handling Null Values in TextView Kotlin Code)
Kotlin has a very safe way to deal with null values. Optional Types act as a wrapper over the current type. They need to be safely unwrapped to use non-null values, thus enabling null safety in our Kotlin code.
Kotlin有一个非常安全的方法来处理空值。 可选类型充当当前类型的包装。 需要安全地解开它们以使用非null值,从而在我们的Kotlin代码中启用null安全性。
Let’s look at how the above app behaves when the textView is null.
让我们看一下当textView为null时上述应用程序的行为。
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
var textView = findViewById<textview>(R.id.textView)
textView.text = null
Log.d(TAG, "TextView text is ${textView.text}") // Logs TextView text is
textView = null
Log.d(TAG, "TextView text is ${textView.text}") //compilation error. Add safe call.
}
So when the text is null, the compiler ignores it.
因此,当文本为null时 ,编译器将忽略它。
When the textView is null, we need to add a safe call to unwrap the textView. This way Kotlin automatically gives us null safety.
当textView为null时 ,我们需要添加一个安全调用以解开textView。 这样Kotlin会自动为我们提供零安全。
What if the textView is null at runtime?
如果textView在运行时为null怎么办?
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
//we've set a random id available from the autocomplete just to set textView to null at runtime.
var textView = findViewById<textview>(R.id.ALT)
Log.d(TAG, "TextView text is ${textView.text}")
}
It will throw error message as IllegalStateException. TextView cannot be null..
它将引发错误消息为IllegalStateException. TextView cannot be null. IllegalStateException. TextView cannot be null. 。
So let’s set the TextView properties as Optional in the declaration.
因此,让我们在声明中将TextView属性设置为Optional。
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val otherTextView: TextView? = findViewById(R.id.textViewOpacity)
otherTextView?.text = null
Log.d(TAG, "TextView displays ${otherTextView?.text ?: "NA"}")
}
We’ve set otherTextView to the type TextView.
我们已经将otherTextView设置为TextView类型。
So calling anything over the TextView would require a safe call.
因此,通过TextView调用任何内容都需要安全的调用。
What if the text is null? What do we display instead?
如果文本为空怎么办? 我们将显示什么呢?
We use the elvis operator ?: from Kotlin for null safety.
我们使用Kotlin的Elvis运算符?:来确保安全。
In the above code, NA gets displayed if otherTextView?.text is null.
在上面的代码中,如果otherTextView?.text为null,则显示NA。
The safe call can be replaced by a let lambda expression too.
安全调用也可以用let lambda表达式代替。
Kotlin Android扩展 (Kotlin Android Extensions)
Thanks to apply plugin: 'kotlin-android-extensions' in our build.gradle file, we can directly bind views from the layout in our Kotlin activity class.
感谢在build.gradle文件中apply plugin: 'kotlin-android-extensions' ,我们可以直接从Kotlin活动类中的布局中绑定视图。
Add the following import statement in your MainActivity.kt class.
在MainActivity.kt类中添加以下导入语句。
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.*
Now you can use the TextView properties directly without using findViewById.
现在,您可以直接使用TextView属性,而无需使用findViewById。
Android TextView Kotlin onClick侦听器 (Android TextView Kotlin onClick Listener)
package net.androidly.androidtextviewkotlin
import android.graphics.Color
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.support.v4.content.ContextCompat
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.*
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
val TAG = "MainActivity"
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
//set textView to clickable
textView.isClickable = true
textView.setOnClickListener{ textView.text = resources.getString(R.string.app_name) }
textViewClickMe.setOnClickListener { textViewClickMe.setTextColor(Color.WHITE) }
textViewEllipsize.ellipsize = TextUtils.TruncateAt.MARQUEE
textViewEllipsize.setHorizontallyScrolling(true)
textViewEllipsize.marqueeRepeatLimit = -1
textViewEllipsize.isSelected = true
val mipMapDrawable = ContextCompat.getDrawable(this, R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
textViewOpacity.setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds(mipMapDrawable,null,mipMapDrawable,null)
}
}
In the above code, for the setOnClickListener we use lambda expressions from Kotlin. It makes the code shorter and easier to read than Java.
在上面的代码中,对于setOnClickListener我们使用来自Kotlin的lambda表达式。 与Java相比,它使代码更短,更易于阅读。
To make the textViewEllipsize slide, set it to MARQUEE. To make it loop continuously, we’ve set marqueeRepeatLimit to -1.
要制作textViewEllipsize幻灯片,请将其设置为MARQUEE。 为了使其连续循环,我们将marqueeRepeatLimit设置为-1。
The mipMapDrawable is of the type Drawable and setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds() is the equivalent of android:drawablePadding.
mipMapDrawable的类型为Drawable,而setCompoundDrawablesWithIntrinsicBounds()等效于android:drawablePadding 。
The app output is shown in the following GIF.
应用程序的输出显示在以下GIF中。
Android TextView扩展功能 (Android TextView extension functions)
We can create Kotlin extension functions on a TextView to add our custom functions and properties.
我们可以在TextView上创建Kotlin扩展功能,以添加自定义功能和属性。
The below extension function creates a consistent property for currentTextColor property and setTextColor() function.
下面的扩展函数为currentTextColor属性和setTextColor()函数创建一致的属性。
Add the following code outside the class.
在类外添加以下代码。
var TextView.textColor: Int
get() = currentTextColor
set(v) = setTextColor(v)
We can then set the color on our TextView using the textColor property.
然后,我们可以使用textColor属性在TextView上设置颜色。
textViewOpacity.textColor = ContextCompat.getColor(this, R.color.colorPrimaryDark)
Android TextView“带有”表达式 (Android TextView “with” expression)
Instead of using redundant lines where we set the attributes on the same TextView property like this:
代替使用多余的行,我们在同一个TextView属性上像下面这样设置属性:
textViewEllipsize.ellipsize = TextUtils.TruncateAt.MARQUEE
textViewEllipsize.setHorizontallyScrolling(true)
textViewEllipsize.marqueeRepeatLimit = -1
textViewEllipsize.isSelected = true
textViewEllipsize.setOnClickListener { println("So many calls to the same TextView") }
We can make it better using the with expression.
我们可以使用with表达式使它更好。
with(textViewEllipsize)
{
ellipsize = TextUtils.TruncateAt.MARQUEE
setHorizontallyScrolling(true)
marqueeRepeatLimit = -1
isSelected = true
setOnClickListener { println("WOW. AWESOME.") }
}
在Kotlin中以编程方式创建TextView (Creating a TextView Programmatically in Kotlin)
Below, we’ve created two TextViews programmatically. We’ve set a custom font from the assets folder and set underline on one of the TextViews. Also, we’ve set the string in the form of HTML.
下面,我们以编程方式创建了两个TextView。 我们从资产文件夹中设置了自定义字体,并在其中一个TextViews上设置了下划线。 另外,我们将字符串设置为HTML形式。
The assets directory is created under src | main folder and is used to hold the TTF files for the custom fonts.
资产目录在src |下创建。 main文件夹,用于保存自定义字体的TTF文件。
package net.androidly.androidtextviewkotlin
import android.graphics.Color
import android.graphics.Paint
import android.graphics.Typeface
import android.os.Build
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.support.v4.content.ContextCompat
import android.text.Html
import android.text.TextUtils
import android.view.Gravity
import android.widget.TextView
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.*
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
val TAG = "MainActivity"
lateinit var programmaticTextView : TextView
var optionalTextView : TextView? = null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
programmaticTextView = TextView(this)
with(programmaticTextView)
{
text = "I'm Created Programmatically. Kotlin makes life simple"
textSize = 20f
textColor = Color.parseColor("#1F2135")
typeface = Typeface.DEFAULT_BOLD
isClickable = true
setOnClickListener { println("I contain the string: $text") }
}
linearLayout.addView(programmaticTextView)
optionalTextView = TextView(this)
optionalTextView.let { with(optionalTextView!!)
{
text = if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N) {
"${Html.fromHtml("
<h4>this is underlined text</h4>
Body goes here",Html.FROM_HTML_MODE_LEGACY)}"
} else {
@Suppress("DEPRECATION")
"${Html.fromHtml("this is <u>underlined</u> text")}"
}
typeface = Typeface.createFromAsset(assets, "Pacifico.ttf")
textSize = 20f
gravity = Gravity.CENTER
paintFlags = Paint.UNDERLINE_TEXT_FLAG
} }
linearLayout.addView(optionalTextView)
}
}
var TextView.textColor: Int
get() = currentTextColor
set(v) = setTextColor(v)
Kotlin properties are required to be initialized there itself. If it’s not possible, we can set a lateinit modifier to the property.
Kotlin属性需要在此处本身进行初始化。 如果不可能,我们可以为属性设置lateinit修饰符。
By default, when the textView is created programmatically, its width is match_parent and height is wrap_content.
默认情况下,以编程方式创建match_parent ,其宽度为match_parent ,高度为wrap_content 。
The paintFlags is used to add an underline to the string.
paintFlags用于在字符串上添加下划线。
The output with the above TextViews added into the layout programmatically is shown in the following image.
下图显示了将上述TextViews以编程方式添加到布局中的输出。
使用可扩展字符串 (Using Spannable Strings)
Spannable Strings are useful when we have to set different styles on different substrings of the TextView.
当我们必须在TextView的不同子字符串上设置不同的样式时,可扩展字符串很有用。
val string = "this is normal, this is underlined"
val firstWord = string.substringBefore(",")
val secondWord = string.substringAfterLast(",")
val redColor = ForegroundColorSpan(
ContextCompat.getColor(this,android.R.color.holo_red_dark))
val ssb = SpannableStringBuilder(firstWord)
ssb.setSpan(
redColor, // the span to add
0, // the start of the span (inclusive)
ssb.length, // the end of the span (exclusive)
Spanned.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE)
ssb.append(" ")
val underlineSpan = UnderlineSpan()
ssb.append(secondWord)
ssb.setSpan(
underlineSpan,
ssb.length - secondWord.length,
ssb.length,
Spanned.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE)
optionalTextView = TextView(this)
optionalTextView.let { with(optionalTextView!!)
{
text = ssb
typeface = Typeface.createFromAsset(assets, "Pacifico.ttf")
textSize = 20f
gravity = Gravity.CENTER
} }
linearLayout.addView(optionalTextView)
Output:
输出:
This brings an end to the comprehensive tutorial on Android TextViews using Kotlin programming.
这结束了使用Kotlin编程的有关Android TextViews的综合教程。
AndroidTextViewKotlin
AndroidTextViewKotlin
翻译自: https://www.journaldev.com/64/android-textview-using-kotlin