以太坊底层通过EVM模块支持合约的执行与调用,调用时根据合约地址获取到代码,生成环境后载入到EVM中运行。通常智能合约的开发流程是用solidlity编写逻辑代码,再通过编译器编译元数据,最后再发布到以太坊上。
代码结构
.
├── analysis.go //跳转目标判定
├── common.go
├── contract.go //合约数据结构
├── contracts.go //预编译好的合约
├── errors.go
├── evm.go //执行器 对外提供一些外部接口
├── gas.go //call gas花费计算 一级指令耗费gas级别
├── gas_table.go //指令耗费计算函数表
├── gen_structlog.go
├── instructions.go //指令操作
├── interface.go
├── interpreter.go //解释器 调用核心
├── intpool.go //int值池
├── int_pool_verifier_empty.go
├── int_pool_verifier.go
├── jump_table.go //指令和指令操作(操作,花费,验证)对应表
├── logger.go //状态日志
├── memory.go //EVM 内存
├── memory_table.go //EVM 内存操作表 主要衡量操作所需内存大小
├── noop.go
├── opcodes.go //Op指令 以及一些对应关系
├── runtime
│ ├── env.go //执行环境
│ ├── fuzz.go
│ └── runtime.go //运行接口 测试使用
├── stack.go //栈
└── stack_table.go //栈验证
指令
OpCode
文件opcodes.go中定义了所有的OpCode,该值是一个byte,合约编译出来的bytecode中,一个OpCode就是上面的一位。opcodes按功能分为9组(运算相关,块操作,加密相关等)。
//算数相关
const (
// 0x0 range - arithmetic ops
STOP OpCode = iota
ADD
MUL
SUB
DIV
SDIV
MOD
SMOD
ADDMOD
MULMOD
EXP
SIGNEXTEND
)
Instruction
文件jump.table.go定义了四种指令集合,每个集合实质上是个256长度的数组,名字翻译过来是(荒地,农庄,拜占庭,君士坦丁堡)估计是对应了EVM的四个发展阶段。指令集向前兼容。
frontierInstructionSet = NewFrontierInstructionSet()
homesteadInstructionSet = NewHomesteadInstructionSet()
byzantiumInstructionSet = NewByzantiumInstructionSet()
constantinopleInstructionSet = NewConstantinopleInstructionSet()
具体每条指令结构如下,字段意思见注释。
type operation struct {
//对应的操作函数
execute executionFunc
// 操作对应的gas消耗
gasCost gasFunc
// 栈深度验证
validateStack stackValidationFunc
// 操作所需空间
memorySize memorySizeFunc
halts bool // 运算中止
jumps bool // 跳转(for)
writes bool // 是否写入
valid bool // 操作是否有效
reverts bool // 出错回滚
returns bool // 返回
}
按下面的ADD指令为例
定义
ADD: {
execute: opAdd,
gasCost: constGasFunc(GasFastestStep),
validateStack: makeStackFunc(2, 1),
valid: true,
},
操作
不同的操作有所不同,操作对象根据指令不同可能影响栈,内存,statedb。
func opAdd(pc *uint64, evm *EVM, contract *Contract, memory *Memory, stack *Stack) ([]byte, error) {
//弹出一个值,取出一个值(这个值依旧保存在栈上面,运算结束后这个值就改变成结果值)
x, y := stack.pop(), stack.peek()
//加运算
math.U256(y.Add(x, y))
//数值缓存
evm.interpreter.intPool.put(x)
return nil, nil
}
gas花费
不同的运算有不同的初始值和对应的运算方法,具体的方法都定义在gas_table里面。 按加法的为例,一次加操作固定耗费为3。
//固定耗费
func constGasFunc(gas uint64) gasFunc {
return func(gt params.GasTable, evm *EVM, contract *Contract, stack *Stack, mem *Memory, memorySize uint64) (uint64, error) {
return gas, nil
}
}
除此之外还有两个定义会影响gas的计算,通常作为量化的一个单位。
//file go-ethereum/core/vm/gas.go
const (
GasQuickStep uint64 = 2
GasFastestStep uint64 = 3
GasFastStep uint64 = 5
GasMidStep uint64 = 8
GasSlowStep uint64 = 10
GasExtStep uint64 = 20
GasReturn uint64 = 0
GasStop uint64 = 0
GasContractByte uint64 = 200
)
//file go-ethereum/params/gas_table.go
type GasTable struct {
ExtcodeSize uint64
ExtcodeCopy uint64
Balance uint64
SLoad uint64
Calls uint64
Suicide uint64
ExpByte uint64
// CreateBySuicide occurs when the
// refunded account is one that does
// not exist. This logic is similar
// to call. May be left nil. Nil means
// not charged.
CreateBySuicide uint64
}
memorySize
因为加操作不需要申请内存因而memorySize为默认值0。
栈验证
先验证栈上的操作数够不够,再验证栈是否超出最大限制,加法在这里仅需验证其参数够不够,运算之后栈是要减一的。
func makeStackFunc(pop, push int) stackValidationFunc {
return func(stack *Stack) error {
//深度验证
if err := stack.require(pop); err != nil {
return err
}
//最大值验证
//StackLimit uint64 = 1024
if stack.len()+push-pop > int(params.StackLimit) {
return fmt.Errorf("stack limit reached %d (%d)", stack.len(), params.StackLimit)
}
return nil
}
}
智能合约
合约是EVM智能合约的存储单位也是解释器执行的基本单位,包含了代码,调用人,所有人,gas相关的信息.
type Contract struct {
// CallerAddress is the result of the caller which initialised this
// contract. However when the "call method" is delegated this value
// needs to be initialised to that of the caller's caller.
CallerAddress common.Address
caller ContractRef
self ContractRef
jumpdests destinations // result of JUMPDEST analysis.
Code []byte
CodeHash common.Hash
CodeAddr *common.Address
Input []byte
Gas uint64
value *big.Int
Args []byte
DelegateCall bool
}
EVM原生预编译了一批合约,定义在contracts.go里面。主要用于加密操作。
// PrecompiledContractsByzantium contains the default set of pre-compiled Ethereum
// contracts used in the Byzantium release.
var PrecompiledContractsByzantium = map[common.Address]PrecompiledContract{
common.BytesToAddress([]byte{1}): &ecrecover{},
common.BytesToAddress([]byte{2}): &sha256hash{},
common.BytesToAddress([]byte{3}): &ripemd160hash{},
common.BytesToAddress([]byte{4}): &dataCopy{},
common.BytesToAddress([]byte{5}): &bigModExp{},
common.BytesToAddress([]byte{6}): &bn256Add{},
common.BytesToAddress([]byte{7}): &bn256ScalarMul{},
common.BytesToAddress([]byte{8}): &bn256Pairing{},
}
执行机
栈
EVM中栈用于保存操作数,每个操作数的类型是big.int,这就是网上很多人说EVM是256位虚拟机的原因。执行opcode的时候,从上往下弹出操作数,作为操作的参数。
type Stack struct {
data []*big.Int
}
func (st *Stack) push(d *big.Int) {
// NOTE push limit (1024) is checked in baseCheck
//stackItem := new(big.Int).Set(d)
//st.data = append(st.data, stackItem)
st.data = append(st.data, d)
}
func (st *Stack) peek() *big.Int {
return st.data[st.len()-1]
}
func (st *Stack) pop() (ret *big.Int) {
ret = st.data[len(st.data)-1]
st.data = st.data[:len(st.data)-1]
return
}
内存
内存用于一些内存操作(MLOAD,MSTORE,MSTORE8)及合约调用的参数拷贝(CALL,CALLCODE)。
内存数据结构,维护了一个byte数组,MLOAD,MSTORE读取存入的时候都要指定位置及长度才能准确的读写。
type Memory struct {
store []byte
lastGasCost uint64
}
// Set sets offset + size to value
func (m *Memory) Set(offset, size uint64, value []byte) {
// length of store may never be less than offset + size.
// The store should be resized PRIOR to setting the memory
if size > uint64(len(m.store)) {
panic("INVALID memory: store empty")
}
// It's possible the offset is greater than 0 and size equals 0. This is because
// the calcMemSize (common.go) could potentially return 0 when size is zero (NO-OP)
if size > 0 {
copy(m.store[offset:offset+size], value)
}
}
func (self *Memory) Get(offset, size int64) (cpy []byte) {
if size == 0 {
return nil
}
if len(self.store) > int(offset) {
cpy = make([]byte, size)
copy(cpy, self.store[offset:offset+size])
return
}
return
}
内存操作
func opMload(pc *uint64, evm *EVM, contract *Contract, memory *Memory, stack *Stack) ([]byte, error) {
offset := stack.pop()
val := evm.interpreter.intPool.get().SetBytes(memory.Get(offset.Int64(), 32))
stack.push(val)
evm.interpreter.intPool.put(offset)
return nil, nil
}
func opMstore(pc *uint64, evm *EVM, contract *Contract, memory *Memory, stack *Stack) ([]byte, error) {
// pop value of the stack
mStart, val := stack.pop(), stack.pop()
memory.Set(mStart.Uint64(), 32, math.PaddedBigBytes(val, 32))
evm.interpreter.intPool.put(mStart, val)
return nil, nil
}
func opMstore8(pc *uint64, evm *EVM, contract *Contract, memory *Memory, stack *Stack) ([]byte, error) {
off, val := stack.pop().Int64(), stack.pop().Int64()
memory.store[off] = byte(val & 0xff)
return nil, nil
}
stateDb
合约本身不保存数据,那么合约的数据是保存在哪里呢?合约及其调用类似于数据库的日志,保存了合约定义以及对他的一系列操作,只要将这些操作执行一遍就能获取当前的结果,但是如果每次都要去执行就太慢了,因而这部分数据是会持久化到stateDb里面的。code中定义了两条指令SSTORE SLOAD用于从db中读写合约当前的状态。
func opSload(pc *uint64, evm *EVM, contract *Contract, memory *Memory, stack *Stack) ([]byte, error) {
loc := common.BigToHash(stack.pop())
val := evm.StateDB.GetState(contract.Address(), loc).Big()
stack.push(val)
return nil, nil
}
func opSstore(pc *uint64, evm *EVM, contract *Contract, memory *Memory, stack *Stack) ([]byte, error) {
loc := common.BigToHash(stack.pop())
val := stack.pop()
evm.StateDB.SetState(contract.Address(), loc, common.BigToHash(val))
evm.interpreter.intPool.put(val)
return nil, nil
}
执行过程
执行入口定义在evm.go中,功能就是组装执行环境(代码,执行人关系,参数等)。
func (evm *EVM) Call(caller ContractRef, addr common.Address, input []byte, gas uint64, value *big.Int) (ret []byte, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {
if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {
return nil, gas, nil
}
// 合约调用深度检查
if evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {
return nil, gas, ErrDepth
}
// balance 检查
if !evm.Context.CanTransfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), value) {
return nil, gas, ErrInsufficientBalance
}
var (
to = AccountRef(addr)
//保存当前状态,如果出错,就回滚到这个状态
snapshot = evm.StateDB.Snapshot()
)
if !evm.StateDB.Exist(addr) {
//创建调用对象的stateObject
precompiles := PrecompiledContractsHomestead
if evm.ChainConfig().IsByzantium(evm.BlockNumber) {
precompiles = PrecompiledContractsByzantium
}
if precompiles[addr] == nil && evm.ChainConfig().IsEIP158(evm.BlockNumber) && value.Sign() == 0 {
return nil, gas, nil
}
evm.StateDB.CreateAccount(addr)
}
//调用别人合约可能需要花钱
evm.Transfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), to.Address(), value)
//创建合约环境
contract := NewContract(caller, to, value, gas)
contract.SetCallCode(&addr, evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(addr), evm.StateDB.GetCode(addr))
start := time.Now()
// Capture the tracer start/end events in debug mode
if evm.vmConfig.Debug && evm.depth == 0 {
evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureStart(caller.Address(), addr, false, input, gas, value)
defer func() { // Lazy evaluation of the parameters
evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureEnd(ret, gas-contract.Gas, time.Since(start), err)
}()
}
//执行操作
ret, err = run(evm, contract, input)
// When an error was returned by the EVM or when setting the creation code
// above we revert to the snapshot and consume any gas remaining. Additionally
// when we're in homestead this also counts for code storage gas errors.
if err != nil {
//错误回滚
evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)
if err != errExecutionReverted {
contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)
}
}
return ret, contract.Gas, err
}
类似的函数有四个。详细区别见最后的参考。
Call A->B A,B的环境独立
CallCode、 和Call类似 区别在于storage位置不一样
DelegateCall、 和CallCode类似,区别在于msg.send不一样
StaticCall 和call相似 只是不能修改状态
Contract和参数构造完成后调用执行函数,执行函数会检查调用的是否会之前编译好的原生合约,如果是原生合约则调用原生合约,否则调用解释器执行函数运算合约。
// run runs the given contract and takes care of running precompiles with a fallback to the byte code interpreter.
func run(evm *EVM, contract *Contract, input []byte) ([]byte, error) {
if contract.CodeAddr != nil {
precompiles := PrecompiledContractsHomestead
if evm.ChainConfig().IsByzantium(evm.BlockNumber) {
precompiles = PrecompiledContractsByzantium
}
if p := precompiles[*contract.CodeAddr]; p != nil {
return RunPrecompiledContract(p, input, contract)
}
}
return evm.interpreter.Run(contract, input)
}
解释器
func (in *Interpreter) Run(contract *Contract, input []byte) (ret []byte, err error) {
//返回数据
in.returnData = nil
var (
op OpCode // 当前指令
mem = NewMemory() // 内存
stack = newstack() // 栈
pc = uint64(0) // 指令位置
cost uint64 // gas花费
pcCopy uint64 // debug使用
gasCopy uint64 // debug使用
logged bool // debug使用
)
contract.Input = input //函数入参
//*****省略******
for atomic.LoadInt32(&in.evm.abort) == 0 {
//获取一条指令及指令对应的操作
op = contract.GetOp(pc)
operation := in.cfg.JumpTable[op]
//valid校验
if !operation.valid {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid opcode 0x%x", int(op))
}
//栈校验
if err := operation.validateStack(stack); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
//修改检查
if err := in.enforceRestrictions(op, operation, stack); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
var memorySize uint64
//计算内存 按操作所需要的操作数来算
if operation.memorySize != nil {
memSize, overflow := bigUint64(operation.memorySize(stack))
if overflow {
return nil, errGasUintOverflow
}
//
if memorySize, overflow = math.SafeMul(toWordSize(memSize), 32); overflow {
return nil, errGasUintOverflow
}
}
// 校验cost 调用前面提到的costfunc 计算本次操作cost消耗
cost, err = operation.gasCost(in.gasTable, in.evm, contract, stack, mem, memorySize)
if err != nil || !contract.UseGas(cost) {
return nil, ErrOutOfGas //超出挂掉
}
if memorySize > 0 {
//如果本次操作需要消耗memory ,扩展memory
mem.Resize(memorySize)
}
// 执行操作
res, err := operation.execute(&pc, in.evm, contract, mem, stack)
if verifyPool {
verifyIntegerPool(in.intPool)
}
// 如果遇到return 设置返回值
if operation.returns {
in.returnData = res
}
switch {
case err != nil:
return nil, err //报错
case operation.reverts: //出错回滚
return res, errExecutionReverted
case operation.halts:
return res, nil //停止
case !operation.jumps: //跳转
pc++
}
}
return nil, nil
}
Solidity案例
和其他语言类似,有了字节码运行机,就可以在字节码上面再组织其他高级语言,而solidlity语言就是实现了这样的语言编译器,方便了合约编写,有利于推广以太坊dapp开发。
pragma solidity ^0.4.17;
contract simple {
uint num = 0;
function simple(){
num = 123;
}
function add(uint i) public returns(uint){
uint m = 111;
num =num * i+m;
return num;
}
}
生成的Opcodes码
JUMPDEST 函数入口
PUSH + JUMPI/JUMP 类似于调用函数
CALLDATASIZE + CALLDATALOAD 大约是获取函数参数
.code
PUSH 80 contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH 40 contract simple {\n uint ...
MSTORE contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH 0 0 //成员变量初始值
DUP1 uint num = 0
//从下面这条指令可以看出,初始化的时候成员变量就会存到statedb里面去
SSTORE uint num = 0
CALLVALUE function simple(){\n nu...
DUP1 olidity ^
ISZERO a
PUSH [tag] 1 a
JUMPI a
PUSH 0 r
DUP1 o
REVERT .17;\n
contra
tag 1 a
//下面部分是构造函数执行的部分
JUMPDEST a
POP function simple(){\n nu...
PUSH 7B 123
PUSH 0 num
DUP2 num = 123
SWAP1 num = 123
//改变成员变量最后都会写入到statedb里面去
SSTORE num = 123
POP num = 123
PUSH #[$] 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 contract simple {\n uint ...
DUP1 contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH [$] 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH 0 contract simple {\n uint ...
CODECOPY contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH 0 contract simple {\n uint ...
RETURN contract simple {\n uint ...
//上面部分做完初始化之后并不会进入到runtime阶段
.data
0:
.code
//下面这段代码大约是处理参数的
PUSH 80 contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH 40 contract simple {\n uint ...
MSTORE contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH 4 contract simple {\n uint ...
CALLDATASIZE contract simple {\n uint ...
LT contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH [tag] 1 contract simple {\n uint ...
JUMPI contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH 0 contract simple {\n uint ...
CALLDATALOAD contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH 100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 contract simple {\n uint ...
SWAP1 contract simple {\n uint ...
DIV contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH FFFFFFFF contract simple {\n uint ...
AND contract simple {\n uint ...
DUP1 contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH 1003E2D2 contract simple {\n uint ...
EQ contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH [tag] 2 contract simple {\n uint ...
JUMPI contract simple {\n uint ...
tag 1 contract simple {\n uint ...
JUMPDEST contract simple {\n uint ...
PUSH 0 contract simple {\n uint ...
DUP1 contract simple {\n uint ...
REVERT contract simple {\n uint ...
tag 2 function add(uint i) public re...
JUMPDEST function add(uint i) public re...
CALLVALUE function add(uint i) public re...
DUP1 olidity ^
ISZERO a
PUSH [tag] 3 a
JUMPI a
PUSH 0 r
DUP1 o
REVERT .17;\n
contra
tag 3 a
JUMPDEST a
POP function add(uint i) public re...
PUSH [tag] 4 function add(uint i) public re...
PUSH 4 function add(uint i) public re...
DUP1 function add(uint i) public re...
CALLDATASIZE function add(uint i) public re...
SUB function add(uint i) public re...
DUP2 function add(uint i) public re...
ADD function add(uint i) public re...
SWAP1 function add(uint i) public re...
DUP1 function add(uint i) public re...
DUP1 function add(uint i) public re...
CALLDATALOAD function add(uint i) public re...
SWAP1 function add(uint i) public re...
PUSH 20 function add(uint i) public re...
ADD function add(uint i) public re...
SWAP1 function add(uint i) public re...
SWAP3 function add(uint i) public re...
SWAP2 function add(uint i) public re...
SWAP1 function add(uint i) public re...
POP function add(uint i) public re...
POP function add(uint i) public re...
POP function add(uint i) public re...
PUSH [tag] 5 function add(uint i) public re...
JUMP function add(uint i) public re...
tag 4 function add(uint i) public re...
JUMPDEST function add(uint i) public re...
PUSH 40 function add(uint i) public re...
MLOAD function add(uint i) public re...
DUP1 function add(uint i) public re...
DUP3 function add(uint i) public re...
DUP2 function add(uint i) public re...
MSTORE function add(uint i) public re...
PUSH 20 function add(uint i) public re...
ADD function add(uint i) public re...
SWAP2 function add(uint i) public re...
POP function add(uint i) public re...
POP function add(uint i) public re...
PUSH 40 function add(uint i) public re...
MLOAD function add(uint i) public re...
DUP1 function add(uint i) public re...
SWAP2 function add(uint i) public re...
SUB function add(uint i) public re...
SWAP1 function add(uint i) public re...
RETURN function add(uint i) public re...
tag 5 function add(uint i) public re...
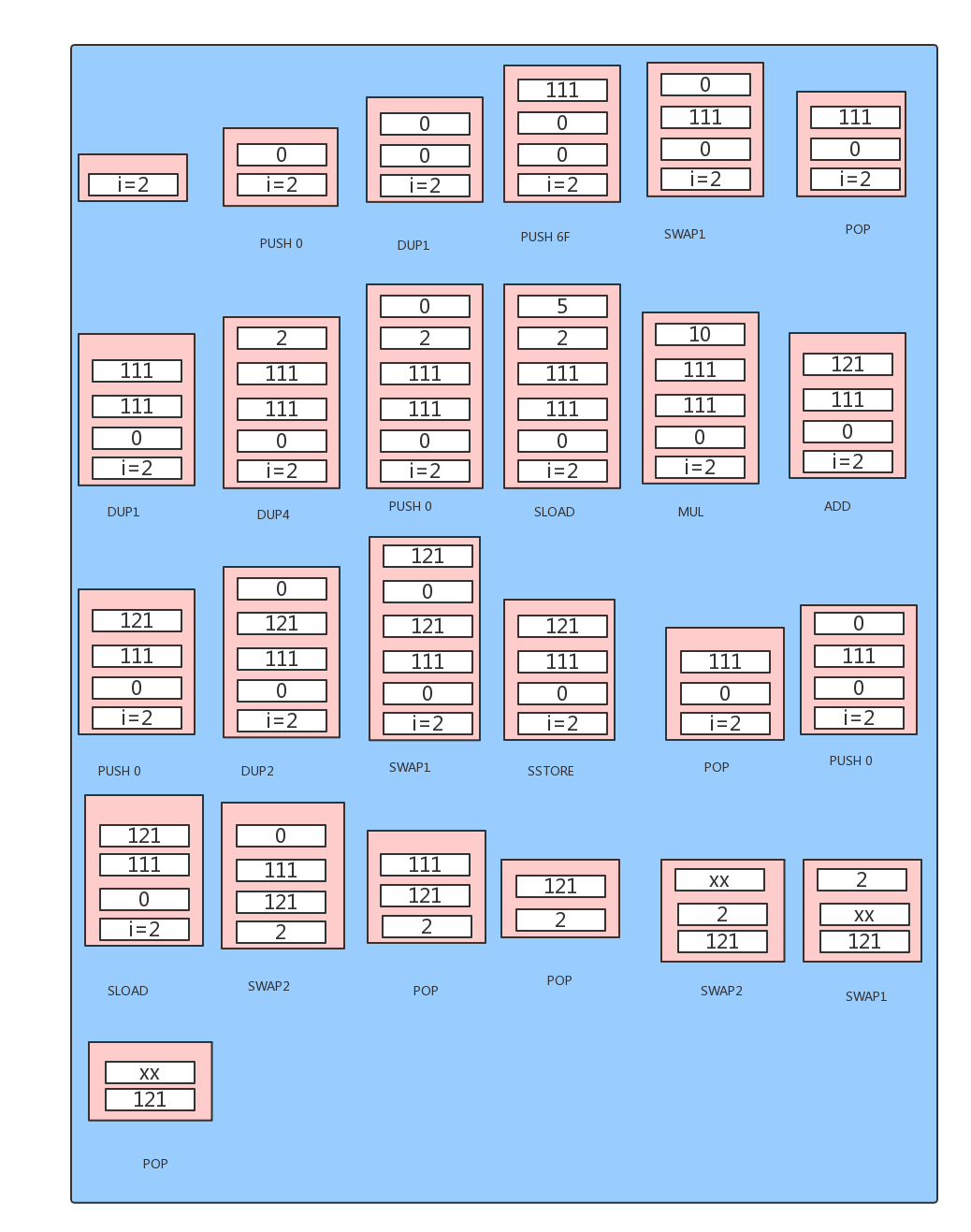
//函数内容
JUMPDEST function add(uint i) public re...
//这下面就是函数的代码了
PUSH 0 uint //局部变量在栈里面
DUP1 uint m
PUSH 6F 111
SWAP1 uint m = 111
POP uint m = 111 //从push0到这里实现了定义局部变量并赋值
DUP1 m
DUP4 i //获取参数
PUSH 0 num
SLOAD num //上面那句和这句实现了读取成员变量
MUL num * i //乘
ADD num * i+m //加
PUSH 0 num
DUP2 num =num * i+m
SWAP1 num =num * i+m //这三句赋值
SSTORE num =num * i+m //成员变量存储
POP num =num * i+m
//下面几句实现return
PUSH 0 num
SLOAD num
SWAP2 return num
POP return num
POP function add(uint i) public re...
SWAP2 function add(uint i) public re...
SWAP1 function add(uint i) public re...
POP function add(uint i) public re...
JUMP [out] function add(uint i) public re...
.data
参考
Call、CallCode、DelegateCall:https://ethereum.stackexchange.com/questions/3667/difference-between-call-callcode-and-delegatecall
solidity结构:https://solidity.readthedocs.io/en/develop/structure-of-a-contract.html#
runtime bytecode和bytecode :https://ethereum.stackexchange.com/questions/13086/solc-bin-vs-bin-runtime/13087#13087
remix: https://remix.ethereum.org/