Store
在 Informer 中 Store 提供了将存储对象的能力,而 Indexer 在 Store 的基础上又提供了可以自定义索引来查询对象的功能
Store 接口提供的功能比较直观,主要是用于对对象的增删改查。包括Indexer、DeltaFIFO等都是实现了Store接口。
// `Store` 接口提供的功能比较直观,主要是用于对对象的增删改查。包括Indexer、DeltaFIFO等都是实现了Store接口
type Store interface {
// Add adds the given object to the accumulator associated with the given object's key
Add(obj interface{}) error
// Update updates the given object in the accumulator associated with the given object's key
Update(obj interface{}) error
// Delete deletes the given object from the accumulator associated with the given object's key
Delete(obj interface{}) error
// List returns a list of all the currently non-empty accumulators
List() []interface{}
// ListKeys returns a list of all the keys currently associated with non-empty accumulators
ListKeys() []string
// Get returns the accumulator associated with the given object's key
Get(obj interface{}) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error)
// GetByKey returns the accumulator associated with the given key
GetByKey(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error)
// Replace will delete the contents of the store, using instead the
// given list. Store takes ownership of the list, you should not reference
// it after calling this function.
Replace([]interface{}, string) error
// Resync is meaningless in the terms appearing here but has
// meaning in some implementations that have non-trivial
// additional behavior (e.g., DeltaFIFO).
Resync() error
}
NewStore 返回Store内部使用线程安全的 map 来存储对象,而 map 的 key 是使用 KeyFunc 函数来计算出来的。
// NewStore 返回Store,内部使用线程安全的 map 来存储对象,而 map 的 key 是使用 KeyFunc 函数来计算出来的。
func NewStore(keyFunc KeyFunc) Store {
return &cache{
cacheStorage: NewThreadSafeStore(Indexers{}, Indices{}),
keyFunc: keyFunc,
}
}
Store的Add方法,使用keyFunc计算出map的key,然后把key和存储的k8s对象放到线程安全的map中。
// Add inserts an item into the cache.
func (c *cache) Add(obj interface{}) error {
key, err := c.keyFunc(obj)
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
c.cacheStorage.Add(key, obj)
return nil
}
MetaNamespaceKeyFunc 是默认的keyFunc,通过 namespace和name来生成存储对象的key,返回 namespace/name,如果 namespace 为空则只返回 name。
// MetaNamespaceKeyFunc 通过 namespace和name来生成存储对象的key,返回 namespace/name,如果 namespace 为空则只返回 name
func MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj interface{}) (string, error) {
if key, ok := obj.(ExplicitKey); ok {
return string(key), nil
}
meta, err := meta.Accessor(obj)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("object has no meta: %v", err)
}
if len(meta.GetNamespace()) > 0 {
return meta.GetNamespace() + "/" + meta.GetName(), nil
}
return meta.GetName(), nil
}
Store的Get方法,使用keyFunc计算出map的key,然后通过key得到完整的存储的k8s对象。
// Get returns the requested item, or sets exists=false.
// Get is completely threadsafe as long as you treat all items as immutable.
func (c *cache) Get(obj interface{}) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error) {
key, err := c.keyFunc(obj)
if err != nil {
return nil, false, KeyError{obj, err}
}
return c.GetByKey(key)
}
Indexer
Indexer 在 Store 的基础上提供了可以自定义索引来查询对象的功能。
type Indexer interface {
Store
// 5、首先会根据索引名称得到对应的索引函数,来计算出 obj 的索引Key,然后再调用 ByIndex得到实际的存储对象
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
// 3、根据索引函数名称获取到相应索引,然后使用索引Key (indexedValue)来获取相应的存储对象的map key,相当于Indices[indexName][indexedValue]
IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)
// 6、返回索引名称 IndexName 下对应索引的所有索引Key
ListIndexFuncValues(indexName string) []string
// 4、首先调用 IndexKeys 得到存储对象的map keys,然后根据map keys从 map 中得到实际的存储对象
ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)
// 1、获取 Indexer 中索引名IndexName和索引函数IndexFunc的map映射
GetIndexers() Indexers
// 2、添加新的索引函数,如果 Indexer 中已经有数据了,实际上会直接报错
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
}
NewIndexer 返回的Indexer内部也是使用线程安全的 map 来存储对象,同时map 的 key 便是使用 KeyFunc 函数来计算出来的。Indexers 则是一组用来根据存储的对象来计算索引 key 的函数。
// NewIndexer 返回的实例内部使用线程安全的 map 来存储对象,而 map 的 key 便是使用 KeyFunc 函数来计算出来的。
// Indexers 是一组用来根据存储的对象来计算索引 key 的函数。
func NewIndexer(keyFunc KeyFunc, indexers Indexers) Indexer {
return &cache{
cacheStorage: NewThreadSafeStore(indexers, Indices{}),
keyFunc: keyFunc,
}
}
// Indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc
// IndexFunc knows how to compute the set of indexed values for an object.
type IndexFunc func(obj interface{}) ([]string, error)
Indexer使用 Indices 来存储索引,Indices 根据 索引名称IndexName对索引进行分类,Index 则是 IndexFunc 计算出来的索引 Key 和存储的map key 的映射关系。同时一个索引 Key 可能对应多个map key,因为根据 IndexFunc 不同的 obj 可能会计算出相同的索引 Key。
// Indices maps a name to an Index
type Indices map[string]Index
// Index maps the indexed value to a set of keys in the store that match on that value
type Index map[string]sets.String
MetaNamespaceIndexFunc是默认的IndexFunc,即根据name的索引。
func MetaNamespaceIndexFunc(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {
meta, err := meta.Accessor(obj)
if err != nil {
return []string{""}, fmt.Errorf("object has no meta: %v", err)
}
return []string{meta.GetNamespace()}, nil
}
tools/cache/listers.go 中的List方法调用的ListAllByNamespace便是利用MetaNamespaceIndexFunc进行查询。
object, err := informerListerForGvr.Lister().ByNamespace("fourier").List(metav1.ListEverythring)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
func (s *genericNamespaceLister) List(selector labels.Selector) (ret []runtime.Object, err error) {
err = ListAllByNamespace(s.indexer, s.namespace, selector, func(m interface{}) {
ret = append(ret, m.(runtime.Object))
})
return ret, err
}
// ListAllByNamespace used to list items belongs to namespace from Indexer.
func ListAllByNamespace(indexer Indexer, namespace string, selector labels.Selector, appendFn AppendFunc) error {
if namespace == metav1.NamespaceAll {
return ListAll(indexer, selector, appendFn)
}
// indexer.Index根据索引名称得到对应的索引函数,来计算出 obj 的索引Key,然后再调用 ByIndex得到实际的存储对象
items, err := indexer.Index(NamespaceIndex, &metav1.ObjectMeta{Namespace: namespace})
if err != nil {
// Ignore error; do slow search without index.
klog.Warningf("can not retrieve list of objects using index : %v", err)
for _, m := range indexer.List() {
metadata, err := meta.Accessor(m)
if err != nil {
return err
}
if metadata.GetNamespace() == namespace && selector.Matches(labels.Set(metadata.GetLabels())) {
appendFn(m)
}
}
return nil
}
selectAll := selector.Empty()
for _, m := range items {
if selectAll {
// Avoid computing labels of the objects to speed up common flows
// of listing all objects.
appendFn(m)
continue
}
metadata, err := meta.Accessor(m)
if err != nil {
return err
}
if selector.Matches(labels.Set(metadata.GetLabels())) {
appendFn(m)
}
}
return nil
}
tools/cache/listers.go 中的Get方法则是直接利用默认的MetaNamespaceKeyFunc ,拼接出map key然后从map中进行取值。
object, err := informerListerForGvr.Lister().ByNamespace("fourier").Get("fourierapp02")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
func (s *genericNamespaceLister) Get(name string) (runtime.Object, error) {
obj, exists, err := s.indexer.GetByKey(s.namespace + "/" + name)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if !exists {
return nil, errors.NewNotFound(s.resource, name)
}
return obj.(runtime.Object), nil
}
ThreadStore
上面讲述了 Store 和 Indexer 的功能,实际上 Indexer 和 Store 都是基于 ThreadSafeStore 来实现的。Store实例和Indexer实例初始化的区别,就是没有 Indexers,Store 算是阉割版的 Indexer。ThreadSafeStore 的操作时需要使用 key 来对对象进行操作的,而 cache 的作用便是使用 cache.keyFunc 来计算对象的 key。
type ThreadSafeStore interface {
Add(key string, obj interface{})
Update(key string, obj interface{})
Delete(key string)
Get(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool)
List() []interface{}
ListKeys() []string
Replace(map[string]interface{}, string)
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)
ListIndexFuncValues(name string) []string
ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)
GetIndexers() Indexers
// AddIndexers adds more indexers to this store. If you call this after you already have data
// in the store, the results are undefined.
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
// Resync is a no-op and is deprecated
Resync() error
}
其具体实现为threadSafeMap
// threadSafeMap implements ThreadSafeStore
type threadSafeMap struct {
// 保证操作 threadSafeMap 的线程安全,全局锁。
lock sync.RWMutex
items map[string]interface{}
// index implements the indexing functionality
index *storeIndex
}
// storeIndex implements the indexing functionality for Store interface
type storeIndex struct {
// Indexers用来存储索引函数,是索引名IndexName和索引函数IndexFunc的map映射,即map[string]IndexFunc
indexers Indexers
// Indices用来存储索引,是索引名IndexName和索引Index的map映射,即map[string]Index
indices Indices
}
threadSafeMap在添加、删除和更新对象时都会更新 indices,简单看一下更新操作
func (c *threadSafeMap) Update(key string, obj interface{}) {
c.lock.Lock()
defer c.lock.Unlock()
oldObject := c.items[key]
c.items[key] = obj
c.index.updateIndices(oldObject, obj, key)
}
// updateIndices modifies the objects location in the managed indexes:
// - for create you must provide only the newObj
// - for update you must provide both the oldObj and the newObj
// - for delete you must provide only the oldObj
// updateIndices must be called from a function that already has a lock on the cache
func (i *storeIndex) updateIndices(oldObj interface{}, newObj interface{}, key string) {
var oldIndexValues, indexValues []string
var err error
for name, indexFunc := range i.indexers {
if oldObj != nil {
// 根据存储对象计算得到旧的索引key
oldIndexValues, err = indexFunc(oldObj)
} else {
oldIndexValues = oldIndexValues[:0]
}
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Errorf("unable to calculate an index entry for key %q on index %q: %v", key, name, err))
}
if newObj != nil {
// 根据存储对象计算得到新的索引key
indexValues, err = indexFunc(newObj)
} else {
indexValues = indexValues[:0]
}
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Errorf("unable to calculate an index entry for key %q on index %q: %v", key, name, err))
}
// 根据索引名找到对应的索引
index := i.indices[name]
if index == nil {
index = Index{}
i.indices[name] = index
}
if len(indexValues) == 1 && len(oldIndexValues) == 1 && indexValues[0] == oldIndexValues[0] {
// We optimize for the most common case where indexFunc returns a single value which has not been changed
continue
}
for _, value := range oldIndexValues {
// key是根据KeyFunc生成的map key,value是旧的索引key,index是索引key和map key的映射关系
i.deleteKeyFromIndex(key, value, index)
}
for _, value := range indexValues {
i.addKeyToIndex(key, value, index)
}
}
}
func (i *storeIndex) deleteKeyFromIndex(key, indexValue string, index Index) {
// key是根据KeyFunc生成的map key,value是旧的索引key,index是索引key和map key的映射关系
// 根据索引key找到所有的存储对象的map key
set := index[indexValue]
if set == nil {
return
}
// sets.String{}是用map实现的数组,提高读写效率
// 从存储对象所有的map key中删除 该对象的map key
set.Delete(key)
// If we don't delete the set when zero, indices with high cardinality
// short lived resources can cause memory to increase over time from
// unused empty sets. See `kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/84959`.
// 如果该索引key下没有map key了,则删除该索引key,防止内存泄漏
if len(set) == 0 {
delete(index, indexValue)
}
}
Index,ByIndex 和 IndexKeys 大致流程相同,都是先判断 indexName 对应的索引函数是否存在,然后从 indices 中获取索引中相应的数据,我们来看一下其中最复杂的 Index 操作。
// Index returns a list of items that match the given object on the index function.
// Index is thread-safe so long as you treat all items as immutable.
func (c *threadSafeMap) Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error) {
c.lock.RLock()
defer c.lock.RUnlock()
storeKeySet, err := c.index.getKeysFromIndex(indexName, obj)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
list := make([]interface{}, 0, storeKeySet.Len())
// 通过存储对象的map key 获取存储对象的完整数据
for storeKey := range storeKeySet {
list = append(list, c.items[storeKey])
}
return list, nil
}
func (i *storeIndex) getKeysFromIndex(indexName string, obj interface{}) (sets.String, error) {
// 先查询索引函数是否存在
indexFunc := i.indexers[indexName]
if indexFunc == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)
}
// 根据索引函数计算存储对象的索引key,如果计算失败,是返回 error
indexedValues, err := indexFunc(obj)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
index := i.indices[indexName]
var storeKeySet sets.String
// obj 只对应一个索引key,那么直接获取该索引key下的所有map key
if len(indexedValues) == 1 {
// In majority of cases, there is exactly one value matching.
// Optimize the most common path - deduping is not needed here.
storeKeySet = index[indexedValues[0]]
} else {
// 根据存储对象所对应的所有索引key,取出保存的map key
// Need to de-dupe the return list.
// Since multiple keys are allowed, this can happen.
storeKeySet = sets.String{}
for _, indexedValue := range indexedValues {
for key := range index[indexedValue] {
storeKeySet.Insert(key)
}
}
}
return storeKeySet, nil
}
Indexer自定义索引的使用
Indexer 具有通过索引函数来自定义索引的能力,那么具体该怎么使用它呢 我们首先定义一个根据 lable 来生成索引的 IndexFunc。
func LabelIndexFunc(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {
metadata, err := meta.Accessor(obj)
if err != nil {
return []string{""}, fmt.Errorf("object has no meta: %v", err)
}
var indexKeys []string
for key, value := range metadata.GetLabels() {
indexKeys = append(indexKeys, key, fmt.Sprintf("%s=%s", key, value))
}
return indexKeys, nil
}
使用 LabelIndexFunc 和 MetaNamespaceIndexFunc 作为索引函数来初始化 Indexer,然后将 pod 对象存到 Indexer 中。
func main() {
indexers := cache.Indexers{
cache.NamespaceIndex: cache.MetaNamespaceIndexFunc,
"labelindex": LabelIndexFunc,
}
indexer := cache.NewIndexer(cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc, indexers)
pods := []*v1.Pod{
&v1.Pod{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: "pod1",
Namespace: "namespace1",
Labels: map[string]string{"label1": "pod1", "label2": "pod1"},
},
},
&v1.Pod{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: "pod2",
Namespace: "namespace2",
Labels: map[string]string{"label1": "pod2"},
},
},
&v1.Pod{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: "pod3",
Namespace: "namespace3",
Labels: map[string]string{"label1": "pod3", "label2": "pod3"},
},
},
}
for _, pod := range pods {
_ = indexer.Add(pod)
}
keys, _ := indexer.IndexKeys(cache.NamespaceIndex, "namespace1")
fmt.Printf("get key by namespace 'namespace1': %v\n", keys)
keys, _ = indexer.IndexKeys("labelindex", "label1")
fmt.Printf("get key by label 'label1': %v\n", keys)
keys, _ = indexer.IndexKeys("labelindex", "label2")
fmt.Printf("get key by label 'label2': %v\n", keys)
keys, _ = indexer.IndexKeys("labelindex", "label1=pod2")
fmt.Printf("get key by label 'label1=pod2': %v\n", keys)
}
得到打印结果。
get key by namespace 'namespace1': [namespace1/pod1]
get key by label 'label1': [namespace1/pod1 namespace2/pod2 namespace3/pod3]
get key by label 'label2': [namespace1/pod1 namespace3/pod3]
get key by label 'label1=pod2': [namespace2/pod2]
总结
Indexers用来存储索引函数,是索引名IndexName和索引函数IndexFunc的map映射。
Indices用来存储索引,是索引名IndexName和索引Index的map映射。
Index是 IndexFunc 计算出来的索引 Key 和存储对象的map key 的映射关系。
IndexFunc是索引函数,根据存储对象计算出来索引key。
keyFunc是存储对象map key的计算函数,根据存储的k8s对象计算出map的key,map的value便是存储的k8s对象。
IndexName索引名称。
indexedValue索引key。
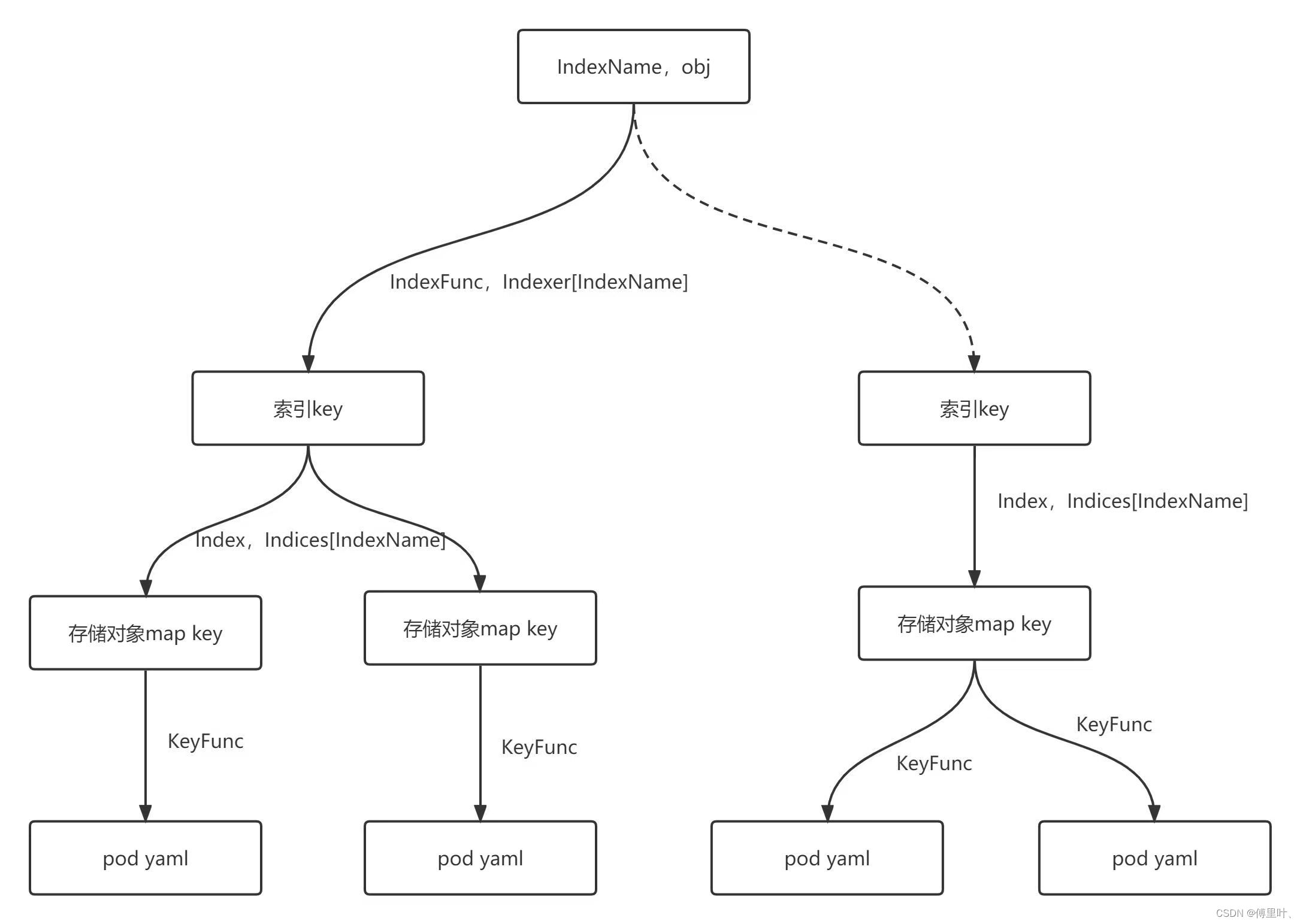
Indexer能够加速返回一批数据的list,对于返回少量数据的list加速不明显。