《Spring 5.x源码解析之Spring AOP 注解驱动使用及其实现原理》
学好路更宽,钱多少加班。---- mercyblitz
一、前言
大家好,欢迎阅读《Spring 5.x源码解析》系列,本篇作为该系列的第二篇,重点介绍Spring AOP在注解驱动编程模式上的使用及其实现原理。文章内容基于小马哥讲 Spring AOP 编程思想以及Spring源码深度解析(第2版)。笔者多次阅读上述学习资料,形成个人关于Spring的知识总结,希望能帮助各位小伙伴!
二、本文概览
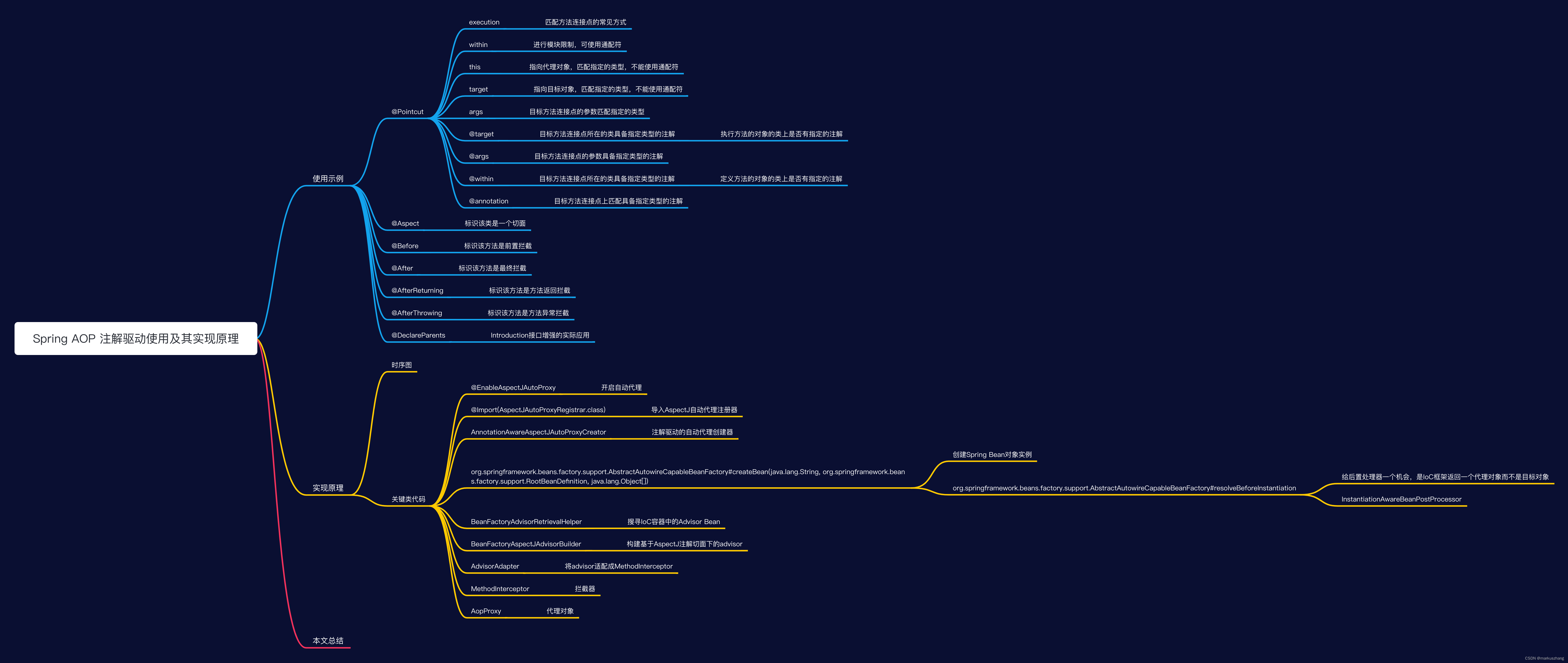
三、使用示例
在本节,我们详细介绍Spring AOP所支持的AspectJ注解使用,在目标方法拦截上介绍@Before、@After、@AfterReturning、@AfterThrowing、@Around、@DeclareParents以及在切入点表达式上介绍execution、within、target、this、args、@args、@target、@within、@annotation的使用
1、@Aspect
该注解的作用就是定义该类是一个切面,在Spring IoC容器会根据Aspect标记拿出该类,创建对应的Advisor,详细动作会在下节实现原理说。
2、AOP通知注解使用
Spring支持AspectJ拦截注解包括@Before、@After、@AfterReturning、@AfterThrowing、@Around,下面简单介绍下他们的作用以及使用方式:
- @Before: 该注解的作用是定义连接点的前置通知方法,在目标方法调用前执行
- @After: 该注解的作用是定义连接点的最终通知方法,在目标方法执行后执行(目标方法正常或异常情况均会执行)
- @AfterReturning: 该注解的作用是定义连接点的后置返回通知方法,在目标方法成功返回后执行
- @AfterThrowing: 该注解的作用是定义在连接点的后置异常返回通知方法,在目标方法执行异常后执行
- @Around: 环绕通知,可以在目标方法执行前后任意时机执行,目标的方法调用是方法内主动去调用,而上面四个注解是被动调用。
下面看下他们的使用示例:
package com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2022/11/29 1:16 PM
* @Description: 前置方法拦截
* @Blog: http://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
@Aspect
public class AspectJAnnotationConfig {
@Before(value = "target(com.markus.aop.overview.EchoService)")
public void before() {
System.out.println("这是前置通知");
}
@After(value = "target(com.markus.aop.overview.EchoService)")
public void after() {
System.out.println("这是方法最终通知");
}
@AfterReturning(value = "target(com.markus.aop.overview.EchoService)")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("这是方法返回通知");
}
@AfterThrowing(value = "target(com.markus.aop.overview.EchoService)")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("这是方法异常通知");
}
@Around(value = "target(com.markus.aop.overview.EchoService)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("这是方法环绕前置通知");
try {
Object obj = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("这是方法环绕返回通知");
return obj;
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("这是方法环绕异常通知");
throw e;
} finally {
System.out.println("这是方法环绕最终通知");
}
}
}
package com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog;
import com.markus.aop.overview.DefaultEchoService;
import com.markus.aop.overview.EchoService;
import com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.aspect.AspectJAnnotationConfig;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2022/11/29 1:20 PM
* @Description: AspectJ注解使用示例
* @Blog: http://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AspectJAnnotationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(AspectJAnnotationDemo.class, AspectJAnnotationConfig.class);
context.refresh();
EchoService echoService = context.getBean(EchoService.class);
echoService.echo("Hello World!");
context.close();
}
@Bean
public EchoService echoService() {
return new DefaultEchoService();
}
}
// 方法正常执行
这是方法环绕前置通知
这是前置通知
[echo] Hello World!
这是方法环绕返回通知
这是方法环绕最终通知
这是方法最终通知
这是方法返回通知
Process finished with exit code 0
// 方法异常执行
这是方法环绕前置通知
这是前置通知
这是方法环绕异常通知
这是方法环绕最终通知
这是方法最终通知
这是方法异常通知
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: 有一定几率异常
at com.markus.aop.overview.DefaultEchoService.echo(DefaultEchoService.java:23)
3、Pointcut切入点表达式
在上面我们看到@Before等等注解内都会有一个value = “target(com.markus.aop.overview.EchoService)”,这个value内容是匹配目标方法的表达式,表达式类型有许多并且也可以通过@Pointcut注解来统一处理,@Before等通知注解引用这个Pointcut即可。下面来逐一介绍下表达式的种类以及其使用方法
- 第一种: execution(modifiers-pattern? ret-type-pattern declare-type-pattern.? name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?)
- 其中带"?"的表示在表达式中可有可无的
- modifiers-pattern 表示方法的访问类型
- ret-type-pattern 表示方法的返回值类型
- declare-type-pattern 表示方法所在类的类型
- name-pattern 表示方法签名
- param-pattern 表示参数的类型
- throws-pattern 表示异常抛出的类型
- 第二种: within(package),对指定模块下的方法进行匹配
- 第三种: this(package.class),对指定类下的方法进行匹配
- package.class 指向代理对象,不可以使用通配符
- 第四种: target(package.class),对指定类下的方法进行匹配
- package.class 指向目标对象,不可以使用通配符
- 第五种: args(ParameterType,…),对指定参数类型的方法进行匹配
- ParameterType 表示目标方法的参数类型
- 第六种: @target(package.class),执行方法所在的对象是否被目标注解定义
- 执行方法的对象,不一定是定义方法的对象,属于运行时匹配,所以@target会将所有原始对象生成代理,所以慎用!
- 第七种: @within(package.class),定义方法所在的对象是否被目标注解匹配
- 第八种: @args(annotationType),目标方法的参数是否被目标注解定义
- annotationType 注解类型,匹配目标方法的参数是否具备目标注解
- 第九种: @annotation(annotationType),目标方法是否被目标注解定义
上面介绍了各种表达式的定义以及作用,下面来介绍下他们的使用方法:
package com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2022/12/1 1:27 PM
* @Description: 横切点表达式使用演示
* @Blog: http://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
@Aspect
public class AspectJPointcutExpressionConfig {
// 表示 方法的访问类型为public 任意返回类型 任意类型的specialReferenceDemo方法 参数可有可无
@Pointcut(value = "execution(public * *.specialReferenceDemo(..))")
public void executionPointcut() {
}
// 表示 匹配在com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog子模块下的方法
@Pointcut(value = "within(com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.domain.*)")
public void withinPointcut() {
}
// 表示 匹配目标对象是com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.domain.DefaultPointcutDemo下的方法
@Pointcut(value = "target(com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.domain.DefaultPointcutDemo)")
public void targetPointcut() {
}
// 表示 匹配代理对象是com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.domain.PointcutDemo下的方法
@Pointcut(value = "this(com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.domain.PointcutDemo)")
public void thisPointcut(){
}
// 表示 匹配的方法中参数是ArgsDemo类型
@Pointcut(value = "args(com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.domain.ArgsDemo)")
public void argsPointcut(){
}
// 表示 匹配被@EchoInterface定义的对象下的方法
// 它是动态匹配的,会为所有目标对象生成代理,所以慎用!例如AOP动态代理通过cglib实现,遇到被final修饰的bean对象,就会抛出异常
@Pointcut(value = "@target(com.markus.aop.overview.annotation.EchoInterface)")
public void atTargetPointcut(){
}
// 表示 匹配被@EchoInterface定义的对象下的方法
// 与@target不同,它是属于静态匹配,描述为定义方法的对象被@EchoInterface注释
@Pointcut(value = "@within(com.markus.aop.overview.annotation.EchoInterface)")
public void atWithinPointcut(){
}
// 表示 匹配参数所属的类型被@EchoInterface注释的所有方法
@Pointcut(value = "@args(com.markus.aop.overview.annotation.EchoInterface)")
public void atArgsPointcut(){
}
// 表示 匹配被@EchoInterface注释的所有方法
@Pointcut(value = "@annotation(com.markus.aop.overview.annotation.EchoInterface)")
public void atAnnotationPointcut(){
}
@Before("executionPointcut()")
public void executionPointcutBefore() {
System.out.println("this is execution pointcut");
}
@Before("withinPointcut()")
public void withinPointcutBefore() {
System.out.println("this is within pointcut");
}
@Before("targetPointcut()")
public void targetPointcutBefore(){
System.out.println("this is target pointcut");
}
@Before("thisPointcut()")
public void thisPointcutBefore(){
System.out.println("this.is this pointcut");
}
@Before("argsPointcut())")
public void argsPointcutBefore(){
System.out.println("this is args pointcut");
}
@Before("atTargetPointcut()")
public void atTargetPointcutBefore(){
System.out.println("this is @target pointcut");
}
@Before("atWithinPointcut()")
public void atWithinPointcutBefore(){
System.out.println("this is @within pointcut");
}
@Before("atArgsPointcut()")
public void atArgsPointcutBefore(){
System.out.println("this is @args pointcut");
}
@Before("atAnnotationPointcut()")
public void atAnnotationPointBefore(){
System.out.println("this is @annotation pointcut");
}
}
package com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog;
import com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.aspect.AspectJPointcutExpressionConfig;
import com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.domain.ArgsDemo;
import com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.domain.DefaultPointcutDemo;
import com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.domain.PointcutDemo;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2022/12/1 10:24 PM
* @Description: 横切点表达式使用示例
* @Blog: http://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AspectJPointcutExpressionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(AspectJPointcutExpressionDemo.class, AspectJPointcutExpressionConfig.class);
context.refresh();
PointcutDemo pointcutDemo = context.getBean(PointcutDemo.class);
ArgsDemo argsDemo = context.getBean(ArgsDemo.class);
System.out.println("-----start-----");
pointcutDemo.specialReferenceDemo(argsDemo);
System.out.println("-----end-----");
context.close();
}
@Bean
public PointcutDemo pointcutDemo() {
return new DefaultPointcutDemo();
}
@Bean
public ArgsDemo argsDemo() {
return new ArgsDemo("Hello World!");
}
}
-----start-----
this is args pointcut
this is @annotation pointcut
this is @args pointcut
this is @target pointcut
this is @within pointcut
this is execution pointcut
this is target pointcut
this.is this pointcut
this is within pointcut
special reference demo content is
-----end-----
Process finished with exit code 0
4、@DeclareParents-接口增强
@DeclareParents可以声明在切面类里,可以起到对拦截器进行增强的作用。下面通过代码演示一下
@Aspect
public class AspectJDeclareParentsConfig {
@DeclareParents(value = "com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.domain.DefaultPointcutDemo", defaultImpl = DefaultUsageTracked.class)
private UsageTracked usageTracked;
@Before("target(com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog.domain.PointcutDemo) && this(usageTracked)")
public void before(UsageTracked usageTracked){
usageTracked.echoMethodInvokeCount();
}
}
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AspectJDeclareParentsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
context.register(AspectJDeclareParentsDemo.class, AspectJDeclareParentsConfig.class);
context.refresh();
PointcutDemo pointcutDemo = context.getBean(PointcutDemo.class);
pointcutDemo.commonDemo("Hello World!");
context.close();
}
@Bean
public PointcutDemo pointcutDemo() {
return new DefaultPointcutDemo();
}
}
1
common demo content is Hello World!
Process finished with exit code 0
四、实现原理
1、时序图
注解驱动实现原理时序图流程可分为三部分来看:
- IoC容器启动过程AOP前期准备-注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
- 用户获取指定的Spring Bean-为当前Bean创建代理对象
- 调用Bean的目标方法-采用动态代理,调用目标方法,在其过程中获取匹配的MethodInterceptor并依次调用实现对目标方法的拦截后,最终通过反射调用目标方法
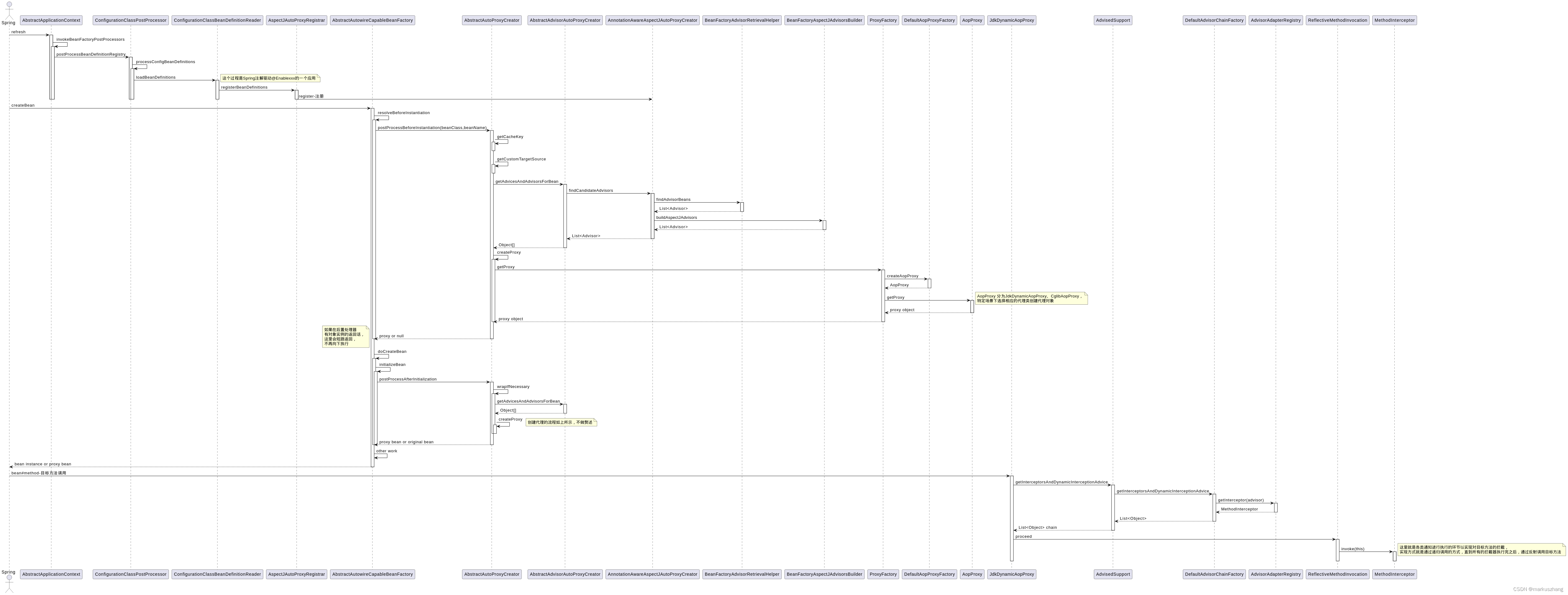
2、关键代码
如上时序图,可以较为清晰的看到Spring是如何给IoC容器中Bean创建代理对象,并且通过代理对象的调用实现对目标方法的拦截。这里再介绍下内部的细节,内容如下:
- Spring是如何开启自动代理的?
- Spring是如何将用户定义的Advice构建为Advisor的?
- Spring是如何创建代理对象的?
- Spring是如何将advisor适配为MethodInterceptor并分配给匹配的方法上的?
- Spring AOP的五种advice执行的先后顺序是如何定义的?
a.Spring是如何开启自动代理的?
Spring通过@EnableAspectJAutoProxy开启AspectJ自动代理,主要是在加载BeanDefinition时动态注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator,使的Bean生命周期中创建Bean实例可以有被代理的机会。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
// 重点在这,通过@Import导入具体的注册器类,在该类下注册相应的BeanDefinition 这也是使用@EnableXXX注解驱动的大致逻辑
@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class)
// 值得注意的是该注解是要注释到配置类上的
public @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy {
/**
* Indicate whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created as opposed
* to standard Java interface-based proxies. The default is {@code false}.
* 可以通过该字段标注Spring是采用jdk动态代理还是CGLIB字节码提升创建代理
* true 使用CGLIB
* false 使用标准方式
*/
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
/**
* Indicate that the proxy should be exposed by the AOP framework as a {@code ThreadLocal}
* for retrieval via the {@link org.springframework.aop.framework.AopContext} class.
* Off by default, i.e. no guarantees that {@code AopContext} access will work.
* @since 4.3.1
* 标识代理是否被可以被当前线程本地缓存 AopContext#setCurrentProxy(proxy)
*/
boolean exposeProxy() default false;
}
- AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar
// 定义AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar 实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的registerBeanDefinitions方法,在加载BeanDefinition的时候注册自定义的BeanDefinition
class AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
/**
* Register, escalate, and configure the AspectJ auto proxy creator based on the value
* of the @{@link EnableAspectJAutoProxy#proxyTargetClass()} attribute on the importing
* {@code @Configuration} class.
*/
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(
AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 向BeanDefinitionRegistry中注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
AnnotationAttributes enableAspectJAutoProxy =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class);
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy != null) {
// @EnableAspectJAutoProxy中的proxyTargetClass配置
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
// @EnableAspectJAutoProxy中的exposeProxy配置
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("exposeProxy")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry);
}
}
}
}
@Nullable
// 在@EnableAspectJAutoProxy中cls指的是的AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(
Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
// 处理Spring中自动代理创建器的优先级问题 如果即将被注册的cls比IoC容器中已存在的自动代理创建器有冲突,则选择优先级最高的进行定义
// 优先级从小到大: InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator < AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator < AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) {
int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName());
int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls);
if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) {
apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName());
}
}
return null;
}
// 无优先级冲突,则创建该类的RootBeanDefinition并注册到BeanDefinitionRegistry中
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
beanDefinition.setSource(source);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);
return beanDefinition;
}
b.Spring是如何将用户定义的Advice构建为Advisor的?
讲述这个问题前,我们先了解下哪些内容可以被Spring认为成Advisor
- IoC容器中注册的Advisor Bean
- IoC容器中注册的Aspect Bean中的Advice method
第一个很好理解,Spring通过依赖查找找到IoC容器注册的Advisor相关Bean,将其加入到List<Advisor>集合中,那第二种Spring是如何进行转换的呢,我们下面来详细了解下
- AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
@Override
@Nullable
// Spring在给Bean创建代理对象时,会为该Bean查找所有的Advice和Advisor
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
// 查找所有符合条件的Advisor
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
// 查找所有符合条件的Advisor
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 查找所有的Advisor
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
// 筛选出符合条件的Advisor
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
// 拓展Advisor,目前在AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator中拓展了此功能,在执行链中增加了ExposeInvocationInterceptor,用于感知目前进行的执行链执行的上下文。
// ExposeInvocationInterceptor拦截器不需要用户感知,只有在AspectJ注解风格下 Spring才会使用
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
// 查询候选的Advisor Bean,子类可以重写此方法来丰富Advisor来源
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
Assert.state(this.advisorRetrievalHelper != null, "No BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper available");
// 这里面就是通过BeanFactory依赖查找Advisor的相关Bean集合,不做赘述了
return this.advisorRetrievalHelper.findAdvisorBeans();
}
- AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
@Override
// 重写AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator中的findCandidateAdvisors方法
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
// 父类提供的查询规则
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
// 基于AspectJ注解,搜寻其切面下的Advice方法 并转换为Advisor
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
}
return advisors;
}
- BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorBuilderAdapter
public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {
// <1> 找到IoC容所有的Aspect Bean名称
List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
synchronized (this) {
aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;
if (aspectNames == null) {
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 也是通过依赖查找,是查找到所有的Bean名称集合
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 遍历所有的Bean名称,排除一些不符合条件的Bean
if (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {
continue;
}
// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this case they
// would be cached by the Spring container but would not have been weaved.
// 这里作者解释了,为什么采用类型查找,而不是实例查找
Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName);
if (beanType == null) {
continue;
}
// 通过AspectJAdvisorFactory判断当前类是否被@Aspect注释
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {
aspectNames.add(beanName);
AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);
if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
// 获取该切面下的所有advisor
List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
// 缓存切面下对应的advisor
this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);
}
else {
// 缓存切面下对应的实例工厂
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
}
advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);
}
else {
// Per target or per this.
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +
"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");
}
// 原型模式
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =
new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);
this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
}
this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;
return advisors;
}
}
}
if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 利用缓存进行性能优化
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {
List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);
if (cachedAdvisors != null) {
advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);
}
else {
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);
advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));
}
}
return advisors;
}
- ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory
@Override
// 通过AspectInstanceFactory获取Advisor集合
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {
Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();
String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();
// <1> 校验切面类
validate(aspectClass);
// We need to wrap the MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory with a decorator
// so that it will only instantiate once.
// 装饰者模式-增强AspectJInstanceFactory功能,使得该切面只被实例化一次
MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =
new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);
List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
// <2> 查找该类下所有的非Pointcut注解的方法
for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {
// <3> 获取Advisor
Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
// If it's a per target aspect, emit the dummy instantiating aspect.
// <4> 如果切面是延迟初始化特性,则在执行链最开始增加一个advisor,直到目标方法被调用时再被初始化
if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {
Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);
advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);
}
// Find introduction fields.
// <5> 接口增强特性-@DeclareParents字段为拦截器增强动作
for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);
if (advisor != null) {
advisors.add(advisor);
}
}
// <6> 返回所有的Advisor数据
return advisors;
}
private List<Method> getAdvisorMethods(Class<?> aspectClass) {
final List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<>();
// 通过反射 查找Advisor目标方法,通过排除Pointcut注解方式实现
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(aspectClass, method -> {
// Exclude pointcuts
if (AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, Pointcut.class) == null) {
methods.add(method);
}
}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
methods.sort(METHOD_COMPARATOR);
return methods;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,
int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {
validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
// 根据候选Advice方法的AspectJ注解 构建AspectJExpressionPointcut
AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(
candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());
if (expressionPointcut == null) {
return null;
}
// 将方法包装为Advisor并返回
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,
this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}
c.Spring是如何创建代理对象的?
Spring创建代理对象是通过ProxyFactory、AopProxyFactory、AopProxy协作创建代理对象
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
// 一般BeanFactory都会走这个流程 将当前Bean的原始类填充到该Bean的BeanDefinition中
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
// <1> ProxyFactory
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
// <2> 将ProxyConfig信息拷贝一份
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
// <3> 是否代理目标类 如果为true 则直接采用CGLIB字节码提升,便没有必要再计算代理接口了。CGLIB是通过生成目标类的子类来进行字节码提升的
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
// <3.1> 是否应该代理目标类 也就是是否采用CGLIB,这是通过BeanDefinition的Attribute属性决定的
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
// <3.2> 计算所要代理的接口
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
// <4> 获取Advisor数组对象
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
// <5> 将Advisor对象添加至代理工厂
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
// <6> 设置目标源
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
// <7> 自定义代理工厂-子类去扩展
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
// <8> 设置代理工厂是否被冻结
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
// <9> 在Advisor匹配时 是否跳过类过滤(ClassFilter)检查
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// <10> 最终创建代理对象并返回
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
// 构建Advisor数组
protected Advisor[] buildAdvisors(@Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors) {
// Handle prototypes correctly...
// 处理指定的拦截器
Advisor[] commonInterceptors = resolveInterceptorNames();
List<Object> allInterceptors = new ArrayList<>();
if (specificInterceptors != null) {
allInterceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(specificInterceptors));
if (commonInterceptors.length > 0) {
if (this.applyCommonInterceptorsFirst) {
allInterceptors.addAll(0, Arrays.asList(commonInterceptors));
}
else {
allInterceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(commonInterceptors));
}
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
int nrOfCommonInterceptors = commonInterceptors.length;
int nrOfSpecificInterceptors = (specificInterceptors != null ? specificInterceptors.length : 0);
logger.trace("Creating implicit proxy for bean '" + beanName + "' with " + nrOfCommonInterceptors +
" common interceptors and " + nrOfSpecificInterceptors + " specific interceptors");
}
Advisor[] advisors = new Advisor[allInterceptors.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < allInterceptors.size(); i++) {
// 通过AdvisorAdapterRegistry将specificInterceptors适配为Advisor
advisors[i] = this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(allInterceptors.get(i));
}
return advisors;
}
// 计算需要代理的接口
protected void evaluateProxyInterfaces(Class<?> beanClass, ProxyFactory proxyFactory) {
// 获取该类的所有接口
Class<?>[] targetInterfaces = ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(beanClass, getProxyClassLoader());
boolean hasReasonableProxyInterface = false;
for (Class<?> ifc : targetInterfaces) {
// 过滤出非Spring内部配置、基建接口并且该接口非标记接口
if (!isConfigurationCallbackInterface(ifc) && !isInternalLanguageInterface(ifc) &&
ifc.getMethods().length > 0) {
hasReasonableProxyInterface = true;
break;
}
}
if (hasReasonableProxyInterface) {
// Must allow for introductions; can't just set interfaces to the target's interfaces only.
// 将可以被代理的接口 添加至ProxyFactory中
for (Class<?> ifc : targetInterfaces) {
proxyFactory.addInterface(ifc);
}
}
else {
// 否则 只能代理目标类
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
}
// 创建AOP代理类
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
// 通过AopProxyFactory创建具体的AOP代理
// AopProxyFactory 默认实现: DefaultAopProxyFactory
// AopProxy : JdkDynamicAopProxy、CglibAopProxy
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}
// 三种条件满足其一,则使用CglibAopProxy
// 1. 配置优化标识被设置为true
// 2. 代理目标类标识被设置为true
// 3. 无代理接口可被使用
// 其余情况均使用JdkDynamicAopProxy
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
剩余的采用JdkDynamicAopProxy以及CglibAopProxy创建代理的步骤就不赘述了。JdkDynamicAopProxy则是使用Proxy.newProxyInstance(xx),CglibAopProxy则是使用Enhancer。
d.Spring是如何将advisor适配为MethodInterceptor并分配给匹配的方法上的?
我们以JdkDynamicAopProxy创建的代理对象为例,介绍该问题。一句话概括就是在调用目标方法时,代理对象进行目标方法的拦截回调invoke,invoke环节里先获取MethodInterceptor执行链,执行链的获取是通过DefaultAdvisorChainFactory获取,在AdvisedSupport中通过PointcutAdvisor筛选出目标的MethodInterceptor获取最终的拦截器执行链,最终通过MethodInvocation#proceed()调用,实现拦截器对目标方法的拦截,内部通过递归调用。
@Override
@Nullable
// 调用目标方法的回调
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
// 获取代理配置的目标源
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;
Object target = null;
try {
// 没有定义equal方法并且当前调用的还是equals方法,则调用代理类实现的equals方法
if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.
return equals(args[0]);
}
// 和equals方法一样的情况
else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.
return hashCode();
}
// 装饰器代理 确定给定实例的最终目标类
else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {
// There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.
return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);
}
// Advise接口上的方法调用
else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);
}
// 上面说的四种情况一般不会进入,一般情况下都是如下流程
Object retVal;
// 1. 是否曝光代理类
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target,
// in case it comes from a pool.
// 获取目标对象
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// Get the interception chain for this method.
// 获取该方法的拦截器执行链,这里是将advisor适配为MethodInterceptor并且返回和方法匹配的MethodInterceptor执行链。
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
// Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct
// reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation.
if (chain.isEmpty()) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does
// nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
// 方法调用前的最后一步: 创建MethodInvocation,它是作为拦截器之间执行传递的媒介
MethodInvocation invocation =
new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
// 方法调用,内部通过递归调用实现拦截器对目标方法的拦截
retVal = invocation.proceed();
}
// Massage return value if necessary.
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&
returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&
!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method
// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets
// a reference to itself in another returned object.
retVal = proxy;
}
else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {
throw new AopInvocationException(
"Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);
}
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
// Must have come from TargetSource.
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method);
// 先去获取缓存,拿到对应的执行链
List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached == null) {
// 缓存中没有 则通过AdvisorChainFactory获取执行链
cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
this, method, targetClass);
// 将执行链添加到缓存中
this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached);
}
return cached;
}
- DefaultAdvisorChainFactory
public class DefaultAdvisorChainFactory implements AdvisorChainFactory, Serializable {
@Override
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
Advised config, Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
// This is somewhat tricky... We have to process introductions first,
// but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list.
// 获取Advisor适配器注册工厂
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();
// 获取配置中的Advisor
Advisor[] advisors = config.getAdvisors();
List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<>(advisors.length);
Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass());
Boolean hasIntroductions = null;
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
// Add it conditionally.
// 下面这一大串则是将配置中Advisor与当前方法进行匹配,如果匹配的上则加入到执行链中,否则跳过
PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
boolean match;
if (mm instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {
if (hasIntroductions == null) {
hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(advisors, actualClass);
}
match = ((IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) mm).matches(method, actualClass, hasIntroductions);
}
else {
match = mm.matches(method, actualClass);
}
if (match) {
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
if (mm.isRuntime()) {
// Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method
// isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains.
for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
// 运行时匹配,创建一个新对象,对象内容包含拦截器和方法匹配器
interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm));
}
}
else {
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
}
}
else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// 需要处理接口增强Advisor
IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
else {
// 其他类型的Advisor
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
return interceptorList;
}
/**
* Determine whether the Advisors contain matching introductions.
*/
private static boolean hasMatchingIntroductions(Advisor[] advisors, Class<?> actualClass) {
for (Advisor advisor : advisors) {
if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;
if (ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
- ReflectiveMethoInvocation
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
// 执行目标连接点
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
e.Spring AOP的五种advice执行的先后顺序是如何定义的?
在上面说到MethodInterceptor执行链,我们知道在注解配置中@Before、@After、@AfterReturning、@AfterThrowing以及@Around对应的方法都会被Spring生成相应的MethodInterceptor,那么他们之间的执行顺序是如何的呢?先来说下结论:
- 不同切面下,advisor所属的切面的优先级谁高谁在前
- 相同切面下,两个advisor如果其中至少一个是AfterAdvice的情况下,谁的声明顺序高(Java Method反射获取方法集合的index)谁在前;两个Advisor均不是AfterAdvice的情况,谁的声明顺序低,谁在前。
下面我们来介绍下:
- AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
// 给Advisor进行排序,该方法是在构建完Advisor集合之后进行调用的
protected List<Advisor> sortAdvisors(List<Advisor> advisors) {
List<PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder> partiallyComparableAdvisors = new ArrayList<>(advisors.size());
for (Advisor element : advisors) {
// 这里面有个关键类DEFAULT_PRECEDENCE_COMPARATOR,也就是AspectJPrecedenceComparator
partiallyComparableAdvisors.add(
new PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder(element, DEFAULT_PRECEDENCE_COMPARATOR));
}
// 进行排序,排序算法我们可以看下AspectJPrecedenceComparator内部的实现
List<PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder> sorted = PartialOrder.sort(partiallyComparableAdvisors);
if (sorted != null) {
List<Advisor> result = new ArrayList<>(advisors.size());
for (PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder pcAdvisor : sorted) {
result.add(pcAdvisor.getAdvisor());
}
return result;
}
else {
return super.sortAdvisors(advisors);
}
}
- AspectJPrecedenceComparator-排序算法
@Override
public int compare(Advisor o1, Advisor o2) {
// 这里依赖AnnotationAwareOrderComparator比较器,该比较器能够得出不同切面内的两个Advisor的优先级
int advisorPrecedence = this.advisorComparator.compare(o1, o2);
// 当两个Advisor之间是相同优先级并且定义在相同切面时,需要区分出优先级
if (advisorPrecedence == SAME_PRECEDENCE && declaredInSameAspect(o1, o2)) {
advisorPrecedence = comparePrecedenceWithinAspect(o1, o2);
}
return advisorPrecedence;
}
// 这里备注下五种Advice的DeclarationOrder
// AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice 4
// AspectJAfterReturningAdvice 3
// AspectJAfterAdvice 2
// AspectJBeforeAdvice 1
// AspectJAroundAdvice 0
private int comparePrecedenceWithinAspect(Advisor advisor1, Advisor advisor2) {
// 两个advisor中是否至少有一个AfterAdvice
boolean oneOrOtherIsAfterAdvice =
(AspectJAopUtils.isAfterAdvice(advisor1) || AspectJAopUtils.isAfterAdvice(advisor2));
// 取出Advisor的声明顺序差
int adviceDeclarationOrderDelta = getAspectDeclarationOrder(advisor1) - getAspectDeclarationOrder(advisor2);
// 如果至少有一个为AfterAdvice
if (oneOrOtherIsAfterAdvice) {
// the advice declared last has higher precedence
// 在两个Advisor中,如果至少其中有一个为AfterAdvice的情况下,谁的DeclarationOrder大 谁的优先级高
if (adviceDeclarationOrderDelta < 0) {
// advice1 was declared before advice2
// so advice1 has lower precedence
return LOWER_PRECEDENCE;
}
else if (adviceDeclarationOrderDelta == 0) {
return SAME_PRECEDENCE;
}
else {
return HIGHER_PRECEDENCE;
}
}
else {
// the advice declared first has higher precedence
// 在两个Advisor中,如果没有AfterAdvice的情况下,谁的DeclarationOrder小,谁的优先极高
if (adviceDeclarationOrderDelta < 0) {
// advice1 was declared before advice2
// so advice1 has higher precedence
return HIGHER_PRECEDENCE;
}
else if (adviceDeclarationOrderDelta == 0) {
return SAME_PRECEDENCE;
}
else {
return LOWER_PRECEDENCE;
}
}
}
五、XML注解驱动实现原理
在写完注解驱动原理后,想另起一篇写一下关于XML配置aop拦截的使用与原理,发现其背后的原理与注解驱动几乎一致,除了配置来源发生变化,一个是基于注解,一个是基于Xml。所以便在本篇文章最后简单说一下在Xml文件中使用aop的示例,原理就不做赘述了,和注解驱动一致。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--开启AspectJ自动代理-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<!--配置切面-->
<bean id="aspectJXmlConfig" class="com.markus.spring.aop.feature.aspect.AspectJXmlConfig"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="aspectJXmlConfig">
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(public * *(..))"/>
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturn" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="throwException" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
<!--注册业务Bean-->
<bean id="echoService" class="com.markus.aop.overview.DefaultEchoService"/>
</beans>
package com.markus.spring.aop.feature.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2022/11/4 11:26 PM
* @Description: 切面,用于xml使用
* @Blog: http://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class AspectJXmlConfig {
public void pointcut() {
}
public void before() {
System.out.println("AspectJXmlConfig#before");
}
public void after() {
System.out.println("AspectJXmlConfig#after");
}
public void afterReturn() {
System.out.println("AspectJXmlConfig#afterReturn");
}
public void throwException() {
System.out.println("AspectJXmlConfig#throwException");
}
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("------around before------");
Object result = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("------around after------");
return result;
}
}
package com.markus.spring.aop.feature.blog;
import com.markus.aop.overview.EchoService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2022/12/4 10:11 PM
* @Description: 基于Xml的aop拦截示例
* @Blog: http://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class AspectJXmlDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/META-INF/spring-aop-advice-application-context.xml");
EchoService echoService = context.getBean(EchoService.class);
echoService.echo("Hello World!");
context.close();
}
}
AspectJXmlConfig#before
------around before------
AspectJXmlConfig#throwException
AspectJXmlConfig#after
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: 有一定几率异常
at com.markus.aop.overview.DefaultEchoService.echo(DefaultEchoService.java:23)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(AopUtils.java:344)
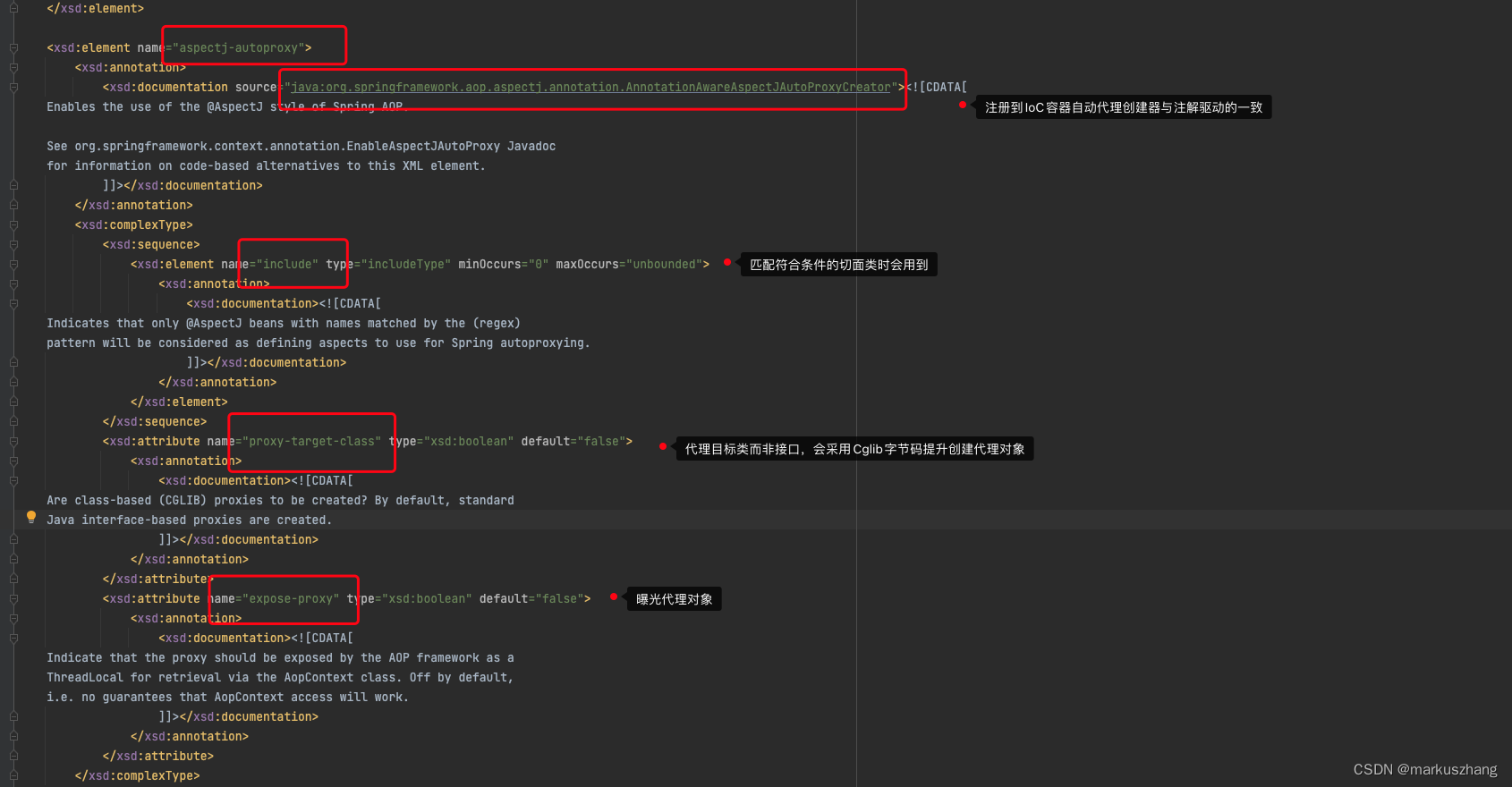
我们可以看到下图中的aspectj-autoproxy标签,与@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解内容一致
六、本文总结
本文对Spring AOP在注解驱动编程模式上的使用及其实现原理进行了详细的介绍,从用户角度实际使用出发,介绍了AspectJ五种Advice注解的使用,并对Pointcut切入点表达式的种类进行了详细的介绍并进行示例演示。介绍完使用后,又对其内部实现原理进行了详细的介绍,以时序图展示Spring在AOP上的实现概览,接着又对其中几处比较重要的实现细节进行了梳理介绍,并且在最后也简要介绍了Xml的使用方式。看完此篇之后,相信大家能够对Spring AOP注解驱动的使用、Xml配置驱动的使用以及其内部原理有个比较好的认知了。下一篇我们将介绍设计模式在Spring AOP中的应用,剖析在框架中应用到的设计模式并且能够将其应用到自己工作中的业务代码,这将是很大的一份收益。