最近刚刚开始学习相机的标定,也是在师兄的帮助下完成的。过程还是值得记录的,于是决定写在自己的第一篇CSDN上,便于之后的复习,同时也希望能够和大家进行交流,相互学习,相互借鉴,达到共同进步的目的!
由于这是我第一次写文章,故有不足之处,希望大家予以批评指正,感激不尽!
对于相机内参的标定,笔者认为可以将其看为一个解方程的过程,也就是说在我们知道空间点 以及其在像素坐标系下的坐标
以及其在像素坐标系下的坐标  ,再根据世界坐标系同相机内部各个坐标系之间的转换关系,来求解相机的内参,从而达到相机内参的标定的目的。下面就让我们先来了解一下各个坐标系之间的转换关系。
,再根据世界坐标系同相机内部各个坐标系之间的转换关系,来求解相机的内参,从而达到相机内参的标定的目的。下面就让我们先来了解一下各个坐标系之间的转换关系。
上文假设一点的空间坐标为 (世界坐标系下的坐标),通过相机的外参矩阵
(世界坐标系下的坐标),通过相机的外参矩阵 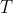 (其中
(其中 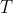 是由旋转矩阵
是由旋转矩阵 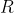 ,平移矩阵
,平移矩阵 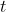 组成的)将点
组成的)将点 转换到相机坐标系下得到点
转换到相机坐标系下得到点 ,公式如下:
,公式如下:

设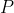 在物理成像坐标系下的坐标为
在物理成像坐标系下的坐标为 ,由相机的成像模型可知
,由相机的成像模型可知


至此得到了空间点 在物理成像平面上的坐标
在物理成像平面上的坐标 。因为这些坐标的单位都是米,要想转换到像素坐标系下还需要通过参数
。因为这些坐标的单位都是米,要想转换到像素坐标系下还需要通过参数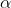 、
、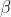 来进行转换,这两个参数的物理意义是单位长度上的像素点的个数,同时考虑到物理成像坐标系和像素坐标系的原点不重合。
来进行转换,这两个参数的物理意义是单位长度上的像素点的个数,同时考虑到物理成像坐标系和像素坐标系的原点不重合。
其中物理成像坐标系的原点在区域中心处,而像素坐标系的原点在左上角,所以有一个偏移量。假设在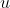 方向上的像素点的偏移量为
方向上的像素点的偏移量为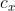 (单位为像素个数),在
(单位为像素个数),在 方向上的像素点的偏移量为
方向上的像素点的偏移量为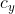 。故可以得到
。故可以得到 的坐标如下所示
的坐标如下所示

进一步的可以得到如下公式

用矩阵的形式可以表示为

有

上式中从左到右参数依次为像素坐标点,相机内参矩阵,变换矩阵(外参矩阵),世界坐标系下的点的坐标。至此理论部分完成,我们所需要做的就是估计出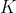 。
。
在ROS(机器人操作系统 Roboat Operating System)下进行相机标定,以下部分为代码部分,作出了部分注解。
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
//首先包含头文件
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//对命名空间的使用
string camera_in_path, camera_folder_path, result_path;
int row_number, col_number, width, height;
//从这里我们可以看出ros::param里面应该有参数
//1.camera_in_path 2.camera_folder_path 3.result_path 4.row_number 5.col_number 6.width 7.height
void getParameters() //该函数是从launch文件中读取参数
{
cout << "Get the parameters from the launch file" << endl;
if (!ros::param::get("camera_in_path", camera_in_path))
{
cout << "Can not get the value of camera_in_path" << endl;
exit(1);
}
if (!ros::param::get("camera_folder_path", camera_folder_path))
{
cout << "Can not get the value of camera_folder_path" << endl;
exit(1);
}
if (!ros::param::get("result_path", result_path))
{
cout << "Can not get the value of result_path" << endl;
exit(1);
}
if (!ros::param::get("row_number", row_number))
{
cout << "Can not get the value of row_number" << endl;
exit(1);
}
if (!ros::param::get("col_number", col_number))
{
cout << "Can not get the value of col_number" << endl;
exit(1);
}
if (!ros::param::get("width", width))
{
cout << "Can not get the value of width" << endl;
exit(1);
}
if (!ros::param::get("height", height))
{
cout << "Can not get the value of height" << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "cameraCalib");//通过ros::init()进行初始化
getParameters();//调用函数获取参数值
ifstream fin(camera_in_path);//相机标定时采用的图像文件的保存路径
ofstream fout(result_path);//相机标定完成保存输出结果的文件路径
//读取每幅图像并从中提取出角点,对其进行呀像素精确化
int image_count = 0; // 图像数量
Size image_size; // 图像的尺寸
Size board_size = Size(row_number, col_number); // 标定板上每行、列的角点数
vector<Point2f> image_points_buf; // 缓存每幅图像上检测到的角点
vector<vector<Point2f>> image_points_seq; // 保存检测到的所有角点
string filename; // 图片名
vector<string> filenames;
while (getline(fin, filename) && filename.size() > 1)
{
++image_count;
filename = camera_folder_path + filename;
cout << filename << endl;
Mat imageInput = imread(filename);
if (imageInput.empty())
{
//利用文件名称来寻找照片
break;
}
filenames.push_back(filename); //将filename存入到filenames中去
// 读入第一张图片时获取图片大小
if (image_count == 1)
{
image_size.width = imageInput.cols;
image_size.height = imageInput.rows;
}
/* 提取角点 */
if (0 == findChessboardCorners(imageInput, board_size, image_points_buf)) //利用Opencv中的函数来寻找角点
{
cout << "**" << filename << "** can not find chessboard corners!\n";
exit(1);
}
else
{
Mat view_gray;
cvtColor(imageInput, view_gray, cv::COLOR_RGB2GRAY); // 转灰度图
/* 亚像素精确化 */
// image_points_buf 初始的角点坐标向量,同时作为亚像素坐标位置的输出
// Size(5,5) 搜索窗口大小
// (-1,-1)表示没有死区
// TermCriteria 角点的迭代过程的终止条件, 可以为迭代次数和角点精度两者的组合
cornerSubPix(view_gray, image_points_buf, Size(5, 5), Size(-1, -1), TermCriteria(cv::TermCriteria::EPS + cv::TermCriteria::MAX_ITER, 30, 0.1)); //Opencv中的函数进行亚像素精确化
image_points_seq.push_back(image_points_buf); // 保存亚像素角点
drawChessboardCorners(view_gray, board_size, image_points_buf, false); // 用于在图片中标记角点
imshow("Camera Calibration", view_gray); // 显示图片
waitKey(1000); //暂停1S
}
}
// int CornerNum = board_size.width * board_size.height; // 每张图片上总的角点数
//-------------以下是摄像机标定------------------
/*棋盘三维信息*/
Size square_size = Size(width, height); /* 实际测量得到的标定板上每个棋盘格的大小 */
vector<vector<Point3f>> object_points; /* 保存标定板上角点的三维坐标 */
/*内外参数*/
Mat cameraMatrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机内参数矩阵 */
vector<int> point_counts; // 每幅图像中角点的数量
Mat distCoeffs = Mat(1, 5, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机的5个畸变系数:k1,k2,p1,p2,k3 */
vector<Mat> tvecsMat; /* 每幅图像的旋转向量 */ //R
vector<Mat> rvecsMat; /* 每幅图像的平移向量 */ //t
/* 初始化标定板上角点的三维坐标 */
int i, j, t;
for (t = 0; t<image_count; t++) //此时的image count为所有图片的个数
{
vector<Point3f> tempPointSet; //存储数据类型为Point3f的点
for (i = 0; i<board_size.height; i++) //标定板上的行
{
for (j = 0; j<board_size.width; j++) //标定板上的列
{
Point3f realPoint; //定义真实空间下的点的坐标
/* 假设标定板放在世界坐标系中z=0的平面上 */
realPoint.x = i * square_size.width; //空间点的X坐标,所在行与单个棋盘格子宽度的乘积
realPoint.y = j * square_size.height; //空间点的Y坐标,所在列与单个棋盘格子高度的乘积
realPoint.z = 0;
tempPointSet.push_back(realPoint); //把得到的点的坐标存入到temp中去
} //一列一列的进行遍历
}
object_points.push_back(tempPointSet);
}
/* 初始化每幅图像中的角点数量,假定每幅图像中都可以看到完整的标定板 */
for (i = 0; i<image_count; i++)
{
point_counts.push_back(board_size.width * board_size.height);
}
/* 开始标定 */
// object_points 世界坐标系中的角点的三维坐标
// image_points_seq 每一个内角点对应的图像坐标点
// image_size 图像的像素尺寸大小
// cameraMatrix 输出,内参矩阵
// distCoeffs 输出,畸变系数
// rvecsMat 输出,旋转向量
// tvecsMat 输出,位移向量
// 0 标定时所采用的算法
calibrateCamera(object_points, image_points_seq, image_size, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvecsMat, tvecsMat, 0);
//------------------------标定完成------------------------------------
// -------------------对标定结果进行评价------------------------------
double total_err = 0.0; /* 所有图像的平均误差的总和 */
double err = 0.0; /* 每幅图像的平均误差 */
vector<Point2f> image_points2; /* 保存重新计算得到的投影点 */
fout << "Average error: \n";
for (i = 0; i<image_count; i++)
{
vector<Point3f> tempPointSet = object_points[i];
/* 通过得到的摄像机内外参数,对空间的三维点进行重新投影计算,得到新的投影点 */
projectPoints(tempPointSet, rvecsMat[i], tvecsMat[i], cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, image_points2);
/* 计算新的投影点和旧的投影点之间的误差*/
vector<Point2f> tempImagePoint = image_points_seq[i];
Mat tempImagePointMat = Mat(1, tempImagePoint.size(), CV_32FC2);
Mat image_points2Mat = Mat(1, image_points2.size(), CV_32FC2);
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < tempImagePoint.size(); j++) {
image_points2Mat.at<Vec2f>(0, j) = Vec2f(image_points2[j].x, image_points2[j].y);
tempImagePointMat.at<Vec2f>(0, j) = Vec2f(tempImagePoint[j].x, tempImagePoint[j].y);
}
err = norm(image_points2Mat, tempImagePointMat, NORM_L2);
total_err += err /= point_counts[i];
fout << "The error of picture " << i + 1 << " is " << err << " pixel" << endl;
}
fout << "Overall average error is: " << total_err / image_count << " pixel" << endl << endl;
//-------------------------评价完成---------------------------------------------
//-----------------------保存定标结果-------------------------------------------
Mat rotation_matrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 保存每幅图像的旋转矩阵 */
fout << "Intrinsic: " << endl;
fout << cameraMatrix << endl << endl;
fout << "Distortion parameters: " << endl;
fout << distCoeffs << endl << endl << endl;
cout << "Get result!" << endl;
fin.close();
fout.close();
return 0;
}
以下是.launch文件的编写
<launch>
<param name="camera_in_path" value="$(find camera_calibration)/data/camera/in.txt"/>
<param name="camera_folder_path" value="$(find camera_calibration)/data/camera/photos/"/>
<param name="result_path" value="$(find camera_calibration)/data/camera/result.txt"/>
<param name="row_number" type="int" value="9"/>
<param name="col_number" type="int" value="6"/>
<param name="width" type="int" value="50"/>
<param name="height" type="int" value="50"/>
<node pkg="camera_calibration" name="camera_calibration" type="camera_calibration" output="screen"/>
</launch>
以下是得到的标定结果
Intrinsic: //相机的内参矩阵
[886.2391758072229, 0, 639.496654129007;
0, 884.5569261594919, 338.8017291870644;
0, 0, 1]
Distortion parameters: //相机的畸变参数
[0.179050927277567, -0.6498127975110598, -0.0004748475598530125, 0.00124291886207487, 0.6813914669391971]
以上皆是在师兄的帮助下完成的,所以要感谢我的师兄~,和大家多多交流,希望大家指出问题,我们共同进步!
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系:hwhale#tublm.com(使用前将#替换为@)